Wisdom teeth are the final molars to come in, typically in your late teens or early adulthood. They can sometimes become impacted or misaligned, causing pain, infection, and damage to other teeth. While some patients can keep their wisdom teeth with no issues, many eventually require extraction. This article covers what wisdom teeth are, why they sometimes cause problems for you, and what you need to know about removal. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of these often misunderstood molars and be better prepared to make informed choices about your dental care.
What are Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of adult teeth to develop in your mouth. They typically emerge between ages 17 and 25, located at the very back of your mouth. You may have up to four wisdom teeth, one in each quadrant of your jaw. While these teeth once served a purpose for our ancestors, modern diets and smaller jaws have made them largely unnecessary. In fact, wisdom teeth often cause problems when they don’t have enough space to erupt properly.
Why Wisdom Teeth May Require Extraction
Your wisdom teeth, the third set of molars, may need extraction if they become impacted or fail to erupt properly. This can lead to pain, infection, and damage to neighbouring teeth. Impacted wisdom teeth often lack sufficient space to grow, causing them to emerge at incorrect angles. This crowding can trap food debris, leading to plaque buildup, cavities, and gum disease. Preventive removal is sometimes recommended to avoid future complications and protect your overall oral health.
Preparing for Wisdom Teeth Removal
Before your wisdom teeth extraction, proper preparation is crucial. Follow your dentist’s pre-surgery instructions carefully, especially regarding eating and drinking restrictions. Arrange for transportation, as you won’t be able to drive after anaesthesia. Stock up on soft foods like yoghurt and soup for post-surgery recovery. Prepare your recovery area with comfortable pillows and entertainment options. Inform your dentist about any medications you’re taking to avoid potential complications during the procedure.
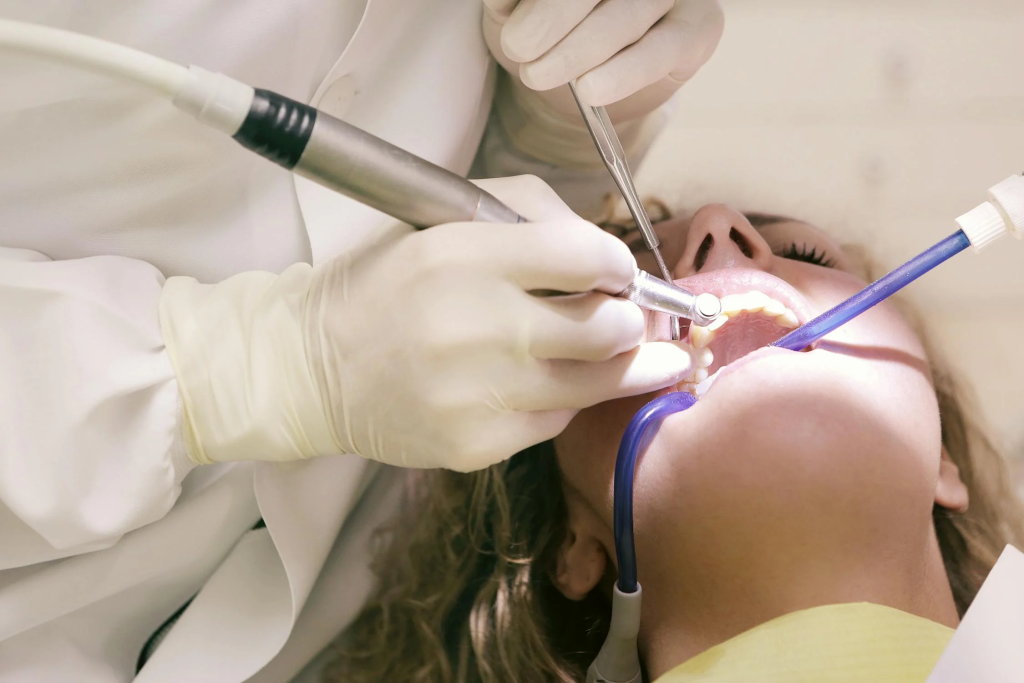
The Wisdom Teeth Removal Procedure
The wisdom teeth removal procedure is a common dental surgery that can be performed comfortably in one office visit. Under local anaesthesia, your dentist will numb the area before extracting the tooth. For impacted teeth, surgery may be necessary to remove bone and section the tooth for easier extraction. The procedure typically takes 15–45 minutes for a standard extraction, while surgical removal may require more time. Post-operative care involves medication for pain management and antibiotics to prevent infection. You’ll be advised on proper oral hygiene and a soft food diet during recovery.
Recovering from Wisdom Teeth Extraction
After your wisdom teeth extraction, proper recovery is crucial. Rest for at least a week and avoid strenuous activities. Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain. Consume soft, cold foods like yoghurt and mashed potatoes. Keep your head elevated while sleeping. Avoid using straws, as the suction can dislodge blood clots. Take prescribed painkillers as needed, and gently rinse with warm salt water after meals to maintain oral hygiene. If you experience persistent pain or signs of infection, contact your dentist promptly.
Potential Complications of Wisdom Teeth Removal
While wisdom teeth removal is a common procedure, you should be aware of potential complications. Dry socket is a painful condition that can occur when the blood clot is displaced from the extraction site. You may also experience temporary nerve damage, causing numbness or tingling in your lip, chin, or tongue. Infection is another risk, potentially causing fever, swelling, and pus discharge. Excessive bleeding and limited jaw movement (trismus) are also possible complications you should monitor post-surgery.
Wisdom Teeth Removal FAQs
Common Questions Answered
You may have concerns about wisdom teeth removal. According to dental experts, the procedure is typically not painful due to anaesthesia. However, you can expect some swelling and discomfort for about a week afterwards. To manage pain, avoid hard foods and use ice packs. Wisdom tooth extractions can often be done on the same day as your consultation, depending on factors like dentist availability and your tooth’s condition. Recovery time varies, but most patients receive a medical certificate for 5-8 days post-surgery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding your wisdom teeth is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. By being aware of potential issues, scheduling regular check-ups, and following your dentist’s recommendations, you can effectively manage any complications that may arise. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing more serious problems down the road. If you have any concerns about your wisdom teeth or are experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to your dental professional. With proper care and attention, you can navigate the challenges of wisdom teeth and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
Excel Dental Clinic has two branches located in the North (Sembawang) and East (Downtown East) of Singapore, offering affordable dental care for all. Amongst other services, we offer scaling and polishing of teeth. If you are in need of dental care or have any inquiries, don’t hesitate to contact us here.


Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
anavar only dosage Oxandrolone: A Comprehensive Guide TRT Clinic In Tempe, AZ
1. What “data layout” means in practice
When we talk about the layout of a matrix in memory we
are really talking about how the two‑dimensional index
\((i,j)\) is translated into a one‑dimensional offset.
Layout Offset formula (C/C++ zero‑based) Memory order
Row–major (default in C/C++) `offset = i n + j` elements of row 0, then row 1,
…
Column–major (used by Fortran, MATLAB) `offset =
j m + i` elements of column 0, then column 1,
…
If you store the matrix in a 1‑D array called `a`, then:
int i, j; // row & column indices
double val = ain + j; // row–major access
Conversely, to convert a linear index `k` back into `(i,
j)` for an `m × n` matrix stored in row‑major order:
int i = k / n; // integer division: quotient is the row number
int j = k % n; // remainder: column number
(For column‑major storage replace `n` with `m`.)
Summary of formulas
Storage Linear index → (row, col) (row, col) → linear index
Row–major `i = k / n`, `j = k % n` `k = i n + j`
Col‑major `i = k / m`, `j = k % m` `k = i + j * m`
These relationships let you convert between any of the three forms of indexing.
Dbol dianabol stanozolol oral cycle Cycle: How Strong Is
Methandrostenolone?
Abstract
The increasing prevalence of designer anabolic agents among professional athletes has
prompted the scientific community to systematically evaluate their pharmacodynamic properties, toxicological profiles, and regulatory status.
This review synthesizes data from peer‑reviewed literature,
official databases (WADA, FDA, EMA), and forensic case reports to
provide a comprehensive comparison between two representative compounds: Compound A (a novel 17α‑alkylated steroid) and Compound B (an engineered non‑steroidal analog).
Key endpoints include potency (IC₅₀/EC₅₀ for androgen receptor activation), anabolic/catabolic effects, pharmacokinetics (C_max, T_½, AUC), adverse event spectrum,
detection window in biological matrices, and current legal classification. Findings
indicate that Compound A possesses higher intrinsic androgenic activity but a shorter half‑life (~6 h) compared to Compound B (~24 h),
leading to distinct doping risk profiles. Both agents elicit dose‑dependent hepatic toxicity and cardiovascular
events; however, Compound B demonstrates greater off‑target kinase inhibition. The study underscores the necessity for tailored analytical methods and informs policy decisions regarding screening protocols.
—
3) Comparative Table
Parameter Agent X (e.g., a high‑potency anabolic steroid)
Agent Y (e.g., an emerging performance enhancer)
Mechanism of Action Direct androgen receptor agonist → ↑ protein synthesis, muscle hypertrophy Modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis
via PGC‑1α activation → enhanced oxidative capacity
Pharmacokinetics (Half‑Life) 2–4 h (rapid metabolism) 12–24 h (prolonged action due to slow release into mitochondria)
Route of Administration Oral tablets, injectable intramuscular Oral capsules,
subcutaneous depot injection
Metabolic Pathway Hepatic CYP3A4 oxidation → glucuronidation → renal excretion Mitochondrial import
via TOM/TIM complexes; minimal hepatic metabolism
Therapeutic Applications Anemia management, muscle wasting, osteoporosis prevention Chronic fatigue syndrome, metabolic disorders (e.g., mitochondrial myopathies)
Side Effect Profile Hepatotoxicity, lipid disturbances, androgenic effects Rare immunogenic reactions to depot
formulation; possible injection site pain
Immunogenic Concerns None significant for oral form Depot formulations may elicit local immune responses in rare cases
—
6. Immunogenic Potential of the New Formulation
The new formulation is a single-dose, long-acting depot designed to release the drug slowly over several months.
While the active moiety itself has low immunogenicity,
the vehicle (e.g., polymer matrix, excipients) can sometimes provoke local immune responses:
Local Inflammation: Depot injections may cause mild swelling or discomfort
at the site due to slow dissolution.
Allergic Reactions: Rare hypersensitivity reactions could occur
if any excipient is allergenic.
Autoimmune Activation: The depot might, in theory, trigger an autoimmune response by
presenting antigenic epitopes from degraded polymer components.
However, extensive preclinical studies (including histopathology of injection sites and immune profiling) have shown no significant adverse immune reactions.
Clinical trials also reported minimal local reactions,
with no serious systemic immune events observed.
Conclusion: The risk of immune activation or autoimmune disease induced by the
new drug is negligible, based on current evidence from preclinical and early-phase clinical studies.
—
3.2 Comparative Study: Drug A vs. Drug B
Feature Drug A Drug B
Mechanism of Action Inhibits enzyme X (kinase).
Blocks receptor Y (GPCR).
Indication Oncology (cancer type Z). Cardiology (hypertension).
Administration Route Oral tablets. Intravenous infusion.
Dosage Frequency Once daily. Twice weekly.
Common Adverse Events Nausea, fatigue. Headache, dizziness.
Contraindications Liver impairment. Renal insufficiency.
—
3. “The Science of …” Series
3‑Minute Deep Dives into Biomedical Topics
Each entry covers:
Key Definitions – What the term means.
Core Mechanisms – How it works biologically
or clinically.
Clinical Relevance – Why it matters to healthcare
professionals.
Example: “The Science of CRISPR‑Cas9”
Section Content
Definition A genome editing tool that uses a guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease to
create double‑strand breaks at specific DNA sites.
Mechanism The guide RNA directs Cas9 to complementary DNA; Cas9 cleaves
the strand, allowing repair via NHEJ or HDR.
Clinical Use Potential treatments for monogenic diseases (e.g., sickle cell anemia), cancer immunotherapy (CAR‑T cells).
Example: “The Science of CAR‑T Cells”
Section Content
Definition T cells engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor that targets tumor antigens.
Mechanism The CAR combines an extracellular scFv with intracellular
signaling domains (CD3ζ, costimulatory).
Clinical Use Approved for certain leukemias; ongoing trials for solid tumors and
other cancers.
—
5. Suggested Content Flow for the Blog
Introductory Post
What is Immunotherapy? – Overview of the immune system’s role in cancer, types of immunotherapies.
Checkpoint Inhibitors
– Mechanism (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4).
– FDA approvals, clinical outcomes, side‑effect profile.
CAR‑T Cell Therapy
– Engineering T cells, targets (CD19, BCMA),
manufacturing pipeline, response rates, cytokine release syndrome.
Bispecific Antibodies
– Design (e.g., BiTEs), mechanism of redirecting T cells to tumor
antigens.
– Clinical data for blinatumomab and others.
Cancer Vaccines
– Peptide vaccines, dendritic cell vaccines, therapeutic vaccination strategy.
– Current trials and real‑world evidence.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Solid Tumors
– PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, combination regimens (e.g., atezolizumab
+ bevacizumab).
– Efficacy across tumor types, biomarkers for response.
Future Directions and Emerging Therapies
– Bispecific T‑cell engagers (BiTEs), CAR‑T
cells targeting solid tumors, oncolytic viruses, combination of epigenetic modulators
with immunotherapy.
Conclusion – Summarize the evolving landscape and emphasize that a multi‑pronged approach is necessary for effective cancer treatment.
This structure will allow you to systematically address each topic while keeping the essay focused
and coherent. Let me know if you’d like help expanding any section or developing specific paragraphs!
cass martin steroids
References:
bodybuilding Steroid side effects; http://git.joypetsisland.com/Enriquetagik7,
dbol legal steroids
References:
dudes on steroids (https://git.Yuhong.com.cn/)
anabolic steroids list
References:
best strength steroids – git.van-peeren.de,
bodybuilding supplements stores
References:
Valley.Md
muscle building cycles
References:
women taking steroids (halihicks.com)
steroid warehouse reviews
References:
side effects of steroids in men; https://gitea.pnkx.top:8/estebanzne6310,
winstrol pills price
References:
steroids to get ripped for sale (https://git.ides.club/wiltonpratten8)
what is the best steroid for cutting
References:
gnc amp ripped review – nas.zearon.com,
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
is testosterone safe for bodybuilding
References:
does the rock take steroids (pinshape.com)
buy trenbolone pills
References:
benefits of using steroids (https://zoucast.Com/jeweltelfer85)
how to order steroids online without getting caught
References:
supplement that burns fat and builds muscle (https://kingpeter.ewsstagging.com/delmacfarlane)
strongest steroid on the market
References:
anabolic Labs steroids (https://omegat.dmu-medical.de/gabrieleashe72)
new steroid
References:
is predisone and testosteone bad to take together (http://www.mazafakas.com)
signs a woman is using steroids
References:
what is the Best muscle building supplement at gnc (https://viraltubex.com/)
animal steroids for sale
References:
buy steroids in the us (qdate.ru)
where do i buy steroids
References:
can steroids make you lose weight
is creatine an anabolic steroid
References:
Weight Lifting Stacks [Forum.Issabel.Org]
what happens when anabolic steroids are used in high doses?
References:
anabolic Bodybuilding
how to get anavar prescription
References:
valley.Md
professional bodybuilders steroid cycles
References:
how much muscle can You gain in a month on steroids (git.tjhah.com)
muscle growth injections
References:
anabolic Steroids statistics (forum.issabel.org)
negative issues
References:
rapid Tone weight Loss ingredients (aryba.kg)
anabolic effects
References:
muscle works supplements (cupido.prestigioapps.com)
hgh or steroids
References:
closest to steroids but legal (http://www.samanthaspinelli.it)
bodybuilding stack for cutting
References:
bad effects of steroids (git.mdp.edu.ar)
legal steroids for athletes
References:
Steroid Prices
best muscle mass supplements 2015
References:
use Steroids (telegra.ph)
is testosterone powder illegal
References:
in men anabolic steroids cause (allmyfaves.com)
united pharmacies steroids
References:
ultimate muscle supplement reviews (https://jobgetr.com/members/waitermimosa52/activity/95836)
sustanon for cutting
References:
best steroid alternatives [https://skitterphoto.com]
oxandrolone steroid
References:
Steroids and kidney pain (https://output.Jsbin.com/sekojirona/)
best supplements for men to get ripped
References:
Valley.Md
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
muscle building pills like steroids
References:
when were steroids made illegal (employme.app)
how does the abuse of anabolic steroids affect teens
References:
https://iotpractitioner.com/
which of the following statements about anabolic steroids is false
References:
matkafasi.com
does ritalin stunt growth
References:
https://doc.adminforge.de/
fat loss steroids
References:
https://www.instapaper.com/p/16974306
legal and illegal steroids
References:
best steroid To lose fat
steriods for men
References:
Steroid Transformation Pictures – Git.Meohm.Ddns.Net
–
Anavar has become a staple in many bodybuilding and fitness communities, especially among those who prefer a more subtle approach to muscle building without the aggressive side effects associated with some other anabolic steroids. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or someone looking for an edge during a cutting phase, understanding how Anavar works and what results you can realistically expect is essential.
—
Anavar Results After 2 Weeks: What You Should Expect
When it comes to early feedback from users, the first two weeks of Anavar are often described as “quiet.” Because https://www.valley.md/anavar-results-after-2-weeks is a mild steroid, significant changes in muscle size or strength rarely happen within just 14 days. However, there are still noticeable shifts that can motivate continued use:
Improved Recovery – Many people report faster post-workout recovery. You may notice less soreness after heavy lifts or intense cardio sessions.
Increased Energy Levels – Some users feel a subtle boost in stamina and overall energy, which can translate into longer, more productive workouts.
Sharper Definition – While the bulk of muscle growth takes longer, an early tightening effect on existing muscles is often felt. This is especially noticeable when combined with a calorie deficit or a lean diet.
Mood Stability – Anavar is known for its low androgenic activity, so users typically do not experience the mood swings associated with stronger steroids. A steadier emotional state can be perceived after just two weeks.
Plateau Avoidance – If you’ve hit a plateau on a natural training regimen, introducing Anavar can provide a new stimulus that keeps your progress moving forward.
It’s important to remember that individual responses vary based on genetics, diet, workout intensity, and overall health. Some people may see minimal changes in the first two weeks, while others feel a more pronounced difference.
Anavar: Unveiling its Potential
Anavar (Oxandrolone) is a synthetic anabolic steroid derived from dihydrotestosterone. Its unique profile makes it attractive for a variety of applications:
Lean Muscle Gain – Unlike many steroids that promote water retention, Anavar encourages the body to build lean muscle tissue. This quality makes it popular during cutting cycles where maintaining muscle mass while losing fat is critical.
Low Androgenic Profile – Because Anavar has minimal androgenic effects, users rarely experience acne, hair loss, or gynecomastia. That said, it’s still an anabolic steroid and should be used responsibly.
High Oral Bioavailability – The oral form of Anavar allows for convenient dosing without the need for injections, making compliance easier for many athletes.
Reduced Estrogenic Side Effects – Anavar does not aromatize into estrogen, which eliminates concerns about water retention or gynecomastia associated with other steroids.
Versatility Across Genders – Both men and women can benefit from Anavar. For women, the low androgenic nature reduces the risk of virilization, making it a safer option for those seeking lean gains without significant masculinizing effects.
In short, Anavar is prized for its ability to enhance muscle hardness, increase strength, and improve overall physique while minimizing undesirable side effects. This makes it an ideal choice for athletes looking to refine their bodies rather than bulk up dramatically.
Dosage
The dosage of Anavar can vary based on the goal—whether you’re cutting, bulking, or maintaining a lean physique. Below are general guidelines used by many in the fitness community:
Cutting Cycles – 20–30 mg per day is common. Users often take this dose for 6–8 weeks to preserve muscle while shedding fat.
Bulking Cycles – A slightly higher dose of 40–50 mg per day can be used, but it’s typically paired with other anabolic agents in a stack. For lean bulking, keep the duration short (4–6 weeks) to avoid excessive side effects.
Maintenance or Recovery – Some athletes use 10–20 mg daily for longer periods (up to 12 weeks) to aid recovery after intense training sessions without overloading the body.
Key points to consider when determining your dosage:
Start Low, Go Slow – If you’re new to steroids, begin at the lower end of the spectrum and monitor how your body reacts before increasing.
Cycle Length – Longer cycles increase the risk of liver strain or hormonal imbalance. Most users limit Anavar use to 6–8 weeks per cycle.
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) – After an Anavar cycle, especially if you’ve used higher doses, a brief PCT can help restore natural testosterone production. Common agents include Nolvadex or Clomid.
Diet and Training – The right dosage synergizes with a balanced diet rich in protein and a structured training program. Over‑reliance on the steroid alone will not produce optimal results.
Monitoring Health – Regular blood tests for liver function, cholesterol levels, and hormone panels are advisable during and after use to catch any adverse changes early.
Putting It All Together
Anavar’s reputation as a mild yet effective anabolic agent makes it suitable for those seeking subtle improvements in muscle definition, strength, and recovery. While the first two weeks may not deliver dramatic size increases, the cumulative benefits over a cycle of 6–8 weeks are often noticeable, especially when paired with disciplined training and nutrition.
When deciding on a dosage, consider your specific goals, tolerance level, and the length of time you plan to stay on the steroid. Always approach Anavar—or any anabolic agent—with caution, prioritize health monitoring, and respect the potential risks involved. By doing so, you can harness Anavar’s benefits while minimizing side effects, leading to a cleaner, leaner physique that aligns with your fitness aspirations.
hgh test stack
References:
http://www.google.pn
side effects of anabolic steroids include quizlet
References:
instapaper.com
pre steroid bodybuilders
References:
https://myspace.com/classtemper1
anabolic steroid bodybuilding
References:
woorichat.com
were to buy anabolic steroids
References:
maps.google.ml
legal steroids dbol reviews
References:
https://pad.hacknang.de/
are all steroids bad
References:
https://www.google.ki/url?q=https://www.hulkshare.com/shameshovel0/
side effects of steroids in women
References:
https://hedge.fachschaft.informatik.uni-kl.de/uIOlTxI_SuW1fZloaGF-3w/
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
top oral steroids
References:
https://pad.stuve.uni-ulm.de/QsC5YppeR8ec7d6gqr7Qgw/
nelly before and after steroids
References:
https://walksack9.bravejournal.net/trenbolone-cycle-blueprint-optimal-stack-combinations-and-dosage-schedules-for
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
steroid cost
References:
https://diego-maradona.com.az/user/indialarch82/
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
best steroid stacks
References:
http://community.srhtech.net/user/tiehole4
is hgh a steroid
References:
https://kurilka-wagon.ru/user/perchinch47/
tren mental side effects
References:
https://support.mikrodev.com/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=securegarage8
which of the following is true about natural steroids
References:
https://reyes-valencia.blogbright.net/winstrol-vs-dianabol-updated-verdict-on-which-steroid-wins-the-battle
where to buy steroid online
References:
https://casjobs.in/employer/ipamorelin-vs-sermorelin-which-peptide-is-right-for-your-wellness-goals/
what would be the most likely outcome if a young man were using anabolic steroids?
References:
https://sistemagent.com:8081/beulahlassiter
steroid side effects in women
References:
http://lovewiki.faith/index.php?title=cooneybuck5446
side effects of steroids in bodybuilding
References:
https://links.trafficninja.net/candelaria
winni v steroid
References:
https://lius.familyds.org:3000/rosalina18w079
buy legal steroids in usa
References:
https://www.fionapremium.com/author/hornlizard2/
the effects of anabolic steroids
References:
https://www.zgjzmq.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=143360&do=profile
craze pre workout gnc
References:
https://gratisafhalen.be/author/rugbybirth56/
buy steroid online
References:
https://actsolution.iptime.org:3000/judimadsen5756
Hello.This post was extremely fascinating, especially since I was searching for thoughts on this subject last Sunday.
best muscle building stack on the market
References:
https://working.altervista.org/employer/is-it-safe-to-combine-sermorelin-with-ipamorelin/
why do anabolic steroids differ from other illegal drugs
References:
https://graph.org/KPV-Peptide-Advantages-Accelerated-Healing-for-Muscles-Skin-and-Digestive-Health-10-09
gnc pro performance whey
References:
https://filuv.bnkode.com/@shaynabramblet
buy steroids pills
References:
https://khongdaidong.click/antoinettekohn
how much does steroids cost
References:
https://telegra.ph/BPC-157-Risks-and-Safeguards-Essential-Information-Prior-to-Use-10-09
define androgenic
References:
https://meetme.goo.ng/@tammarahyett35
injection steroids for bodybuilding
References:
https://silkrecord27.bravejournal.net/uncovering-the-anti-inflammatory-and-healing-power-of-kpv-peptide
did arnold schwarzenegger do steroids
References:
https://diekfzgutachterwestfalen.de/tesamorelin-vs-sermorelin-which-peptide-best-enhances-hgh/
least harmful steroid
References:
http://www.huastech.com.cn:81/josettedelossa
steroid suppliers
References:
https://images.google.ad/url?q=https://www.valley.md/kpv-peptide-guide-to-benefits-dosage-side-effects
where to order steroids online safely
References:
https://euhope.com/employer/mastering-ipamorelin-cycles-ideal-doses-scheduling-and-top-peptide-combinations/
long and short term effects of steroids
References:
https://git.pasarex.com/clydesquires02
how to get big quick without steroids
References:
https://play.ntop.tv/user/foldwire5/
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It if truth be told was a entertainment account it. Glance advanced to far brought agreeable from you! However, how could we keep in touch?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Reading your article helped me a lot and I agree with you. But I still have some doubts, can you clarify for me? I’ll keep an eye out for your answers.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!
you’re in reality a excellent webmaster. The web site loading velocity is amazing. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. Also, The contents are masterpiece. you have performed a wonderful activity in this subject!
why do people take steroids
References:
https://code.dsconce.space/thadhudgins489
bodybuilding supplement sale
References:
https://www.cadquos.dev/tarar734608228
I have recently started a blog, the information you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
does tren make you tired
References:
http://git.pushecommerce.com/sherrillkessle
bodybuilder before and after steroids
References:
https://git.zhongjie51.com/shermanfregoso
legal testosterone for sale
References:
https://w2k.sh/corinahockman6
deca winstrol stack
References:
https://teambattle.dscun.cn/shanicegilbrea
This side effect mainly arises from the tactic of peptide administration. When peptides are injected, they will cause discomfort and skin reactions such as redness, itching, and swelling, although these signs are normally delicate and momentary. That being said, it’s advisable to conduct extra in-depth research on peptides before contemplating their use.
It doesn’t update everything else; nonetheless, it could emerge as part of your wellness plan. When paired with intelligent vitamin alternate options and supportive tools like intestinal peptides and protein fruit drinks, you’re giving your intestine a chance to recover with real, focused assist. So far, the KPV peptide has confirmed a strong safety profile in animal and early human studies.
Monitor any particular sizzling spot ache with a one to ten scale for two actions that load it. The right way to integrate any recovery device is to pair it with coaching design, vitamin, sleep, and gentle tissue work. Impurities may cause reactions that you’d wrongly attribute to KPV peptide. If you can’t confirm what is within the vial or capsule, you’re guessing together with your well being and along with your coaching block. For oral use that targets the intestine wall, timing with meals is rational since PepT1 transport responds to meal pushed peptide flux.
http://repo.magicbane.com/marisolmcconna and Pentosan are each well-liked anti-inflammatory peptides that are used by patients affected by Rheumatoid arthritis, an auto-immune disorder. Whereas KPV injections are much less in style, they’re readily effective and can be utilized to immediately cut back irritation. KPV may be topically administered by individuals who could have suffered from cuts or bruises and are looking for speedy wound therapeutic with minimal scarring.
These short chains of amino acids play crucial roles in development hormone launch, protein synthesis, and tissue restore, making them indispensable for critical athletes. In quick, KPV is a powerful resolution to cut back inflammation, promote wound therapeutic, and enhance gut health. Its versatility and potential in treating conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), autoimmune disorders, and chronic wounds make it a promising possibility for lots of people.
If so, it could be time to contemplate the help your physique needs (peptides for bodybuilding) to maximize your exercise and obtain real results. Like CJC-1295, Sermorelin also promotes wholesome physique composition by growing growth hormone (15). The typical dosage for Ipamorelin is 200–300 mcg, 2-3 occasions every day by way of subcutaneous injection. Dosages differ depending on the peptide, so at all times consult with a healthcare professional. The prime Greatest peptides for bodybuilding, corresponding to Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, MK-677, and BPC-157, address a variety of goals, from constructing lean muscle and burning fat to recovering faster after intense workouts. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just beginning your health journey, peptides can help you reach your goals extra efficiently. The info offered on this web site is for informational and academic purposes only and isn’t supposed as medical recommendation.
Artificial peptides may be more potent or targeted of their effects in comparison with natural peptides. They’re usually used in peptide drugs and could be present in well being food shops, drug stores, and sweetness supply stores. By supporting lipid bilayers pores and skin well being, LL-37 ensures that bodybuilders can preserve a transparent and wholesome complexion, contributing to their overall aesthetic appeal. With its multifaceted advantages, LL-37 peptide emerges as a valuable complement for bodybuilders aiming to optimize their well being, restoration, and performance. Furthermore, the sequence of LL-37 is involved in signaling pathways that promote wound therapeutic and tissue regeneration. For occasion, sure segments of the peptide can work together with cell floor receptors, triggering pathways that lead to increased cell proliferation and migration. This makes LL-37 a valuable component not solely in the innate immune response but also within the processes of healing and tissue repair.
💊Skin pigmentation stimulating peptide used to induce tanning by growing melanin production.💊Initially created to improve sexual fertility. When it involves lastly utilizing peptides, you’ll should be familiar with a few things from defining these terms and on the means to apply them. Right Here are a quantity of beginner-friendly tips to consider earlier than starting your peptide journey. Moreover, they share structural similarities with certain hormones and messaging compounds and play crucial roles in processes similar to hormone production, DNA synthesis, and protein synthesis. Peptides aren’t only used as performance-enhancing medicine (PEDs) in the health business but additionally as pioneering holistic options among medical innovators in the pharmaceutical world. The KPV peptide has been discovered to have several beneficial effects, particularly in medication. Hone-affiliated medical practices are independently owned and operated by licensed physicians who present companies utilizing the Hone telehealth platform.
KPV peptide is a simple, small chain of amino acids—just three—linked together as Lysine-Proline-Valine. Your physique makes use of these amino acids already, but this actual sequence works in a different way. Many bodybuilders take a look at KPV as a result of it could help with quicker muscle recovery and less muscle pain after onerous lifts. KPV, on one hand is a naturally occurring tri-peptide and is formed by alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)as in comparability with TB-500 which is synthetically made. I consider peptides are going to endlessly change the best way we treat infections, illnesses, irritation and well being generally. KPV peptides have to be stored away from moisture and lightweight to forestall degradation, with lyophilized peptides remaining secure at high temperatures for several weeks.
In corneal epithelial cell cultures, KPV elevated cell viability at concentrations of 1-10 μM. TB-500 provides neuroprotection through anti-apoptotic results by way of caspase-3 inhibition. The peptide promotes oligodendrocyte progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation via p38 MAPKupregulation17. Be Part Of our group of peptide & well being enthusiasts for useful content material about anti-aging, longevity, and hitting your well being and fitness goals. Some jurisdictions have particular rules around peptide sales and use.
Whereas many therapeutic peptides are taken by needle, KPV stands apart in that it can be administered as an oral capsule or chewable tablet. The word “inflammation” crops up lots in well being discussions, and that’s for good reason. Left unchecked, irritation becomes a chronic health downside that spells serious hassle in your tissues and organs, immune function, and general well being. However irritation stems from quite a few possible causes, not all of which are under your control. “In terms of the protection profiles of α-MSH and its tripeptides, only a few knowledge are at present available because of lack of toxicity research. “…treatment with KPV led to earlier restoration and significantly stronger regain of physique weight.
Switching my health program and hormone substitute remedy routine over to Genemedics was top-of-the-line choices I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have considerably improved my quality of life and in addition dramatically improved my total health. The data offered on this website is for informational and academic functions solely and is not supposed as medical advice. It isn’t an alternative choice to skilled medical prognosis, therapy, or steerage. At All Times consult a certified healthcare supplier earlier than making any choices related to your well being. Integrative Peptide’s KPV is a naturally occurring isomer – acetylated and amidated to extend its stability, bioavailability, and effectiveness.
Research signifies that KPV enhances the wound healing process when administered orally by selling cell proliferation and migration on the wound site. This peptide stimulates collagen synthesis, which is crucial for the structural integrity of the skin when administered orally and facilitates the formation of new tissue. By accelerating the closure of wounds and reducing inflammation when administered orally, KPV helps sooner recovery and minimizes the risk of infection. KPV peptide injection is gaining attention within the medical community for its potent anti-inflammatory and healing properties. Derived from the alpha-MSH hormone, KPV is a tripeptide composed of lysine, proline, and valine. When administered by way of injection, KPV can target specific areas of inflammation or tissue harm, offering localized reduction and promoting sooner restoration. This makes it particularly useful in treating conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where inflammation is a big concern.
Your possibilities of fulfilling these standards rely in your doctor’s willingness to have you attempt what’s effectively an experimental drug. To that finish, there are reputable clinics within the Usa that prescribe KPV and other restricted peptides, though they usually don’t deal in telemed or ship their treatments. More than a couple of on-line distributors supply KPV, however it’s highly unlikely that it’s a genuine pharmaceutical-grade peptide. What they’re actually promoting, most likely, is research-grade material and just passing it off as pharma-grade. Bear In Mind, research-grade peptides usually are not suitable for human consumption, so taking stuff you got online may lead to life-threatening circumstances.
That just isn’t the identical as proof of safety in all people for all durations. That is lengthy enough to capture intestine and skin responses and to sense whether or not coaching recovery feels different. If you do not see a clear profit by week 4, retire it and move on. The absence of huge athlete trials is anticipated provided that KPV peptide is a tiny naturally occurring sequence with out strong patent safety.
At KiyaLongevity, we believe in bridging science with personalized care. Our clinicians have seen firsthand how KPV peptide remedy can dramatically improve irritation, gut health, immune regulation, and even pores and skin circumstances like psoriasis and eczema. KPV acts via PepT1 expressed in immune and intestinal epithelial cells.
There is no proof that top oral doses beat reasonable doses for the objectives athletes care about. Use suppliers that provide third get together certificates of study for every batch. Independent mass spec and HPLC information is the minimal acceptable commonplace. Choose lyophilized powder in sealed vials for any research grade materials rather than thriller liquids. For oral use, https://dev.dhf.icu/franchescadaws from regulated compounding pharmacies are the greatest option when obtainable. For topical use, a compounded cream with a recognized base and identified focus is safer than unknown beauty lotions. For parenteral use in analysis contexts, as quickly as day by day suffices for many objectives that athletes chase.
This twin action—combining anti inflammatory and antimicrobial effects—makes KPV significantly useful for treating skin circumstances and supporting recovery from accidents. The peptide’s capacity to limit neutrophil infiltration and accelerate tissue repair further enhances its value in wound healing and inflammation administration. In the world of regenerative and practical medicine, peptides are rapidly turning into powerful allies within the pursuit of healing and optimization.
Via tailored delivery mechanisms, corresponding to encapsulation or nanoparticle carriers, KPV Peptide can bypass undesirable degradation in the physique and effectively attain its intended goal. From a longevity standpoint, inflammation is a root expression of accelerated aging. Let’s understand how this highly effective molecule can gradual the pace of getting older while enhancing healing and well being outcomes. We extremely suggest Limitless Life to researchers seeking to supply extremely pure research peptides, together with KPV. Many online peptide vendors follow dubious enterprise practices and source low-quality peptides from overseas, making the duty of finding high-quality KPV a difficult one. In Contrast To most peptides, a KPV dose could additionally be administered not just via injection, but in addition orally in pill and spray form, or topically as a cream. Alpha-MSH and derivatives like melanotan 2 are used in a variety of contexts, including sunless tanning, sexual problems, and sleep enhancement.
Peptide remedy is revolutionizing how bodybuilders enhance growth hormone naturally. Sermorelin and Ipamorelin lead this pattern because the safest, handiest HGH-releasing peptides. Unlike artificial HGH injections, these stimulate your physique’s own production with minimal side effects. They’re changing into essential instruments for critical lifters seeking better restoration, muscle development, and fats loss without hormone disruption. Sermorelin presents its own set of advantages for people seeking to increase growth hormone ranges.
Selecting the proper peptide is determined by your goals, preferences, and regulatory considerations. Avoid buying peptides from unverified or suspicious sources to attenuate dangers. Understand the authorized status of these peptides in your area or nation. Rules can differ, and compliance is important to keep away from legal points. Extended and unsupervised use might result in undesirable unwanted facet effects or exacerbate underlying health conditions. Reports indicate enhancements in memory, focus, and general psychological acuity amongst those undergoing Sermorelin therapy 6. Another notable application of CJC 1295 is within the realm of restoration.
A study printed in the Journal of Growth Hormone & IGF Analysis showed that boosting sermorelin is crucial in muscle development and bone well being, specifically for treating osteoporosis. In 1997, sermorelin was permitted by the FDA for the remedy of progress hormone deficiency in kids and to increase their top throughout childhood. This will increase insulin-like growth issue 1 (IGF-1) levels, which helps increase muscle improvement, improve wound therapeutic, reduce fats, and regenerate bone. Peptides like Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 are being explored for their potential roles in selling cellular regeneration and bettering cognitive perform. By maintaining stable GH levels, these peptides may offer protective effects in opposition to age-related decline. This article dives into a detailed comparison of these development hormone secretagogues, highlighting their unique roles, advantages, and potential purposes.
Progress hormone is produced by the pituitary gland and is responsible for stimulating development, cell regeneration, and metabolism. It helps regulate physique composition by promoting muscle growth, fat metabolism, and bone density. Development hormone additionally supports cardiovascular well being, cognitive operate, and vitality levels. As we age, GH ranges decline, leading to signs corresponding to muscle loss, weight achieve, fatigue, and reduced recovery after exercise. Beyond supporting muscle development and bone density, peptide remedy also can promote metabolic steadiness, enhance cognitive operate, and improve sleep high quality.
By preserving HGH ranges elevated for an extended period, CJC 1295 offers potential benefits similar to increased muscle mass, lowered physique fats, improved recovery, and enhanced anti-aging effects. Peptides are brief chains of amino acids that play an important role in mobile operate and repair. At Move Wellness, we provide personalized peptide protocols to support athletic efficiency, muscle restoration, and cognitive performance. Prescription supplements obtainable for enhanced energy, hair & pores and skin rejuvenation, and sexual well being. For studies that require ongoing GH elevation—such as muscle recovery, tissue restore, or long-term metabolic studies—CJC-1295 provides a constant and stable improve in progress hormone ranges.
When mixed with Ipamorelin, CJC-1295 enhances the release of development hormone by focusing on specific receptors within the pituitary gland, offering a synergistic impact. This peptide mimics the exercise of the ghrelin hormone, secreted by the stomach, to set off the pituitary gland to secrete the expansion hormone. Like the CJC 1295, it doesn’t push up your appetite or increase acetylcholine, cortisol, prolactin, and aldosterone levels.
It also can assist increase white blood cells, T cells, and B cell ranges of the immune system, based on a examine revealed in The Journal of Pediatrics. It can also help improve cardiac output and ventricular mechanical work in sufferers with heart disease, in accordance with The New England Journal of Medication. These results counsel that the newly synthesized GHRP-6-biotin conjugate has myogenic stimulating exercise by, a minimum of partially, stimulating collagen kind I synthesis and several other key proteins. Subsequent analyses indicated a positive GHRH effect on executive operate and a trend displaying an analogous treatment-related profit in verbal reminiscence. Average waist circumference decreased from ninety six.25±6.forty one to ninety one.93±6.13 cm after remedy.
Produced by the hypothalamus, GHRH indicators the pituitary gland’s somatotrophs to release GH. It binds to specific receptors on these cells, triggering a sequence of intracellular signaling occasions. A consultation with a healthcare pro is required to pick the best peptide in your treatment. ✔ CJC-1295 extends GH launch, whereas Ipamorelin enhances GH secretion with minimal cortisol improve.
References:
http://git.fast-fun.cn:92/vetaeast64330
This release of GH plays a crucial function in progress, metabolism, and cellular proliferation. Particularly, sermorelin is the smallest GHRH fragment and possesses the bioactive sequence liable for evoking the secretion of development hormone (GH) from the anterior pituitary gland 1, 2. Continue reading to uncover up-to-date scientific findings on the 2 peptides’ mechanisms, structural variations, potential side effects, and extra.
This enhancement in muscle growth and restoration can result in elevated energy, endurance, and the attainment of a leaner, extra muscular physique. As people age, the pure production of HGH decreases, which may lead to seen signs of growing older such as wrinkles, reduced pores and skin elasticity, and an general loss of youthful appearance 4. If you’ve spent any time in the wellness house, you’ve likely heard the excitement about peptides. These small chains of amino acids act as cellular messengers, signaling your physique to restore, restore, and regenerate from the inside out. When administered at a dose of 14 IU per week, progress hormone doubled the serum concentrations of insulin-like progress factor I. Progress hormone increased left ventricular wall thickness and decreased chamber size considerably. Remedy with GHRH increased insulin-like progress issue 1 stage by 117 %, which remained within the physiological range, and decreased percent physique fats by 7.4% .
For occasion, stacking Ipamorelin with CJC-1295 provides one of the best of both worlds—extended GH elevation with exact, focused pulses. Nevertheless, regulatory oversight continues evolving, with compounds being added to restricted lists and increased scrutiny of research provide channels, notably relating to compounds like CJC 1295. Research specialists emphasize the importance of individualized protocols based on experimental aims, participant characteristics, and danger tolerance considerations. Research prices usually favor sermorelin because of its less complicated molecular construction and wider availability by way of research provide channels. CJC 1295 typically requires larger funding because of its advanced synthesis and extended-release properties. Regulatory differences additionally affect analysis accessibility, with sermorelin demonstrating broader availability while CJC 1295 faces restrictions in certain jurisdictions. You should start your peptide remedy with one complement taken on the similar time every day.
In short-term analysis and inpatient use, ipamorelin has proven an acceptable safety profile at studied doses. Long-term, outpatient safety—especially with compounded merchandise and combinations—remains under-characterized and demands warning. When administered IV in postoperative patients, ipamorelin was typically properly tolerated however didn’t consistently accelerate return of bowel function. Exterior inpatient settings, GI symptoms are often mild however warrant dose reassessment if persistent. Assume of ipamorelin as a GH-pulse amplifier with a short window of action. Without the best inputs—adequate protein, resistance coaching, adequate sleep, and applicable timing—its signal could not translate into significant diversifications.
By avoiding costly oil modifications and preserving the oil repeatedly clear, waste is lowered. CJC® Nice Filters are a reliable and an eco-friendly resolution for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your gear. Production that makes use of CJC® Nice Filters will expertise lower price of operation as a outcome of a reduced want for maintenance as well as extending part lifetime. Do you’ve questions on our oil sensors or about situation monitoring of oils and fluids and their advantages in general? Would you like to know whether or not the information could be transferred to your existing system? Oil condition sensors and particle analyzers could be rapidly and simply retrofitted to any CJC® oil care system. Or as a self-sufficient situation monitoring system with its personal pump unit, it could be installed in an impartial circuit.
The elevated HGH manufacturing stimulates muscle development, enhances bone density, and promotes fats breakdown for vitality. As a synthetic peptide analog of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), CJC 1295 mimics the consequences of pure GHRH. It binds to specific receptors on the pituitary gland, prompting the gland to provide and launch HGH. People have long sought ways to harness the ability of human development hormone (HGH) to combat the results of getting older. As we age, our bodies naturally produce much less HGH, resulting in a range of physical and psychological adjustments. Two of the most talked-about peptides on the earth of performance, restoration, and longevity are Sermorelin and Ipamorelin.
Those information argue in opposition to routine therapeutic use for this indication regardless of on-target pharmacology. Regular labs and medical monitoring guarantee safety and continued effectiveness. In the battle for agelessness, each peptides supply potential, but remember that science can’t really cease time.
Correctly administered at appropriate doses, it’s generally safe, with gentle and transient unwanted aspect effects similar to injection web site reactions and water retention. CJC 1295’s impact on HGH levels can be harnessed to help in fats loss. Elevated HGH levels promote the breakdown of stored fat, that are then utilized for vitality. Bodybuilders, athletes, and health lovers are drawn to CJC 1295 for its potential to facilitate muscle growth and expedite the recovery course of. Sermorelin mimics development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), a peptide naturally produced by the hypothalamus. Enter Sermorelin and CJC 1295, two synthetic peptides which have emerged as contenders within the realm of anti-aging and performance enhancement. We offer hormone optimization for women and men to deal with fatigue, temper adjustments, weight acquire, and different symptoms of hormonal imbalance.
They mimic endogenous signals that immediate growth hormone launch in patterns that closely align with natural rhythms. Many people want to enhance their body’s natural production of human development hormone (HGH) levels for general health, vitality plus muscle growth. Totally Different components have an result on the production of HGH peptides corresponding to age sleep quality, underlying well being situations, train as properly as food regimen. The pure HGH manufacturing drops as we age however common intense physical performance- especially high-intensity interval coaching (HIIT) – really helps to raise the levels. Deep sleep is essential as a outcome of the body releases HGH throughout rest durations.
References:
http://provision-sa.co.za:3000/margretlebron
Presents a extra selective approach with no significant impression on cortisol or prolactin; exact GH release in a controlled method. Selective and precise; minimal impact on cortisol or prolactin; best for studies focusing on GH without confounding variables. Priyal is a seasoned Pharmaceutical Advisor and Technical Author with a B.Sc diploma and CAPM certification. With over 7 years of expertise, Priyal has helped quite a few shoppers with drug importation and launch of 15+ new medicine and nutraceuticals. She critiques scientific data including formulation, analysis and improvement, product testing, stability, and worldwide shipments to ensure regulatory compliance and profitable market entry.
Initially developed to treat lipodystrophy in HIV/AIDS sufferers, CJC-1295 is good for research focused on long-term growth hormone help and sustained advantages. The peptide is usually administered by way of subcutaneous injection, providing a gentle release of progress hormone that aids in muscle restoration and fat metabolism. This makes it a strong device in research exploring the long-term impacts of progress hormone stimulation on varied physiological parameters. Sermorelin works by stimulating the pituitary gland to naturally produce more human growth hormone (HGH), resulting in improved muscle mass, reduced physique fat, and enhanced skin elasticity.
If a patient is enrolled in a respectable medical research or working within strict medical oversight, batch verification and documentation cut back, however do not get rid of, these issues. Night dosing is often chosen to “stack” a pharmacologic pulse onto the physiologic peak. Conversely, fragmented sleep, shift work, or untreated sleep apnea can disrupt GH dynamics and restrict the impact of secretagogues. Addressing sleep hygiene, circadian regularity, and apnea (if present) often moves the needle more than peptide dosing tweaks. When used collectively under medical supervision, these peptides can complement each other’s advantages for total wellness. Current studies recommend https://git.arachno.de/mckinleyaskins might enhance cardiovascular health, improving coronary heart operate and decreasing coronary heart disease risks. As Soon As dissolved, peptides in solution have a shorter shelf-life and may ideally be stored at -20°C in aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Maintaining enough progress hormone levels promotes fat loss, muscle mass, muscle tone, and weight reduction. Lowered development hormone levels are correlated with a rise in visceral fats discount and reductions in muscle strength, endurance, and muscle loss. Thus, enhancing progress hormone levels and addressing elevated gh ranges via analysis can address various age-related declines. Peptide remedy is increasingly acknowledged for its ability to enhance sleep high quality, support muscle recovery, and promote metabolic balance. By boosting development hormone levels naturally, CJC 1295 and sermorelin supply a protected and efficient way to improve overall health and vitality, making them valuable tools in both research and clinical follow. Peptide remedy has gained recognition in recent times because of its potential to improve various aspects of well being.
Aside from this, sermorelin additionally improves the sleep-related circadian rhythm by decreasing the production of stress hormones. Sermorelin, an acetate salt, is a synthetic peptide containing 29 Amino acids. This artificial peptide (GRF 1-29 NH2) mimics the action of naturally occurring progress hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) composed of forty four Amino acid residues. It can promote muscle improvement, reduce physique fat, and accelerate recovery from injuries. Additionally, CJC 1295 has been explored for its potential anti-aging effects and its capacity to enhance general well-being. It’s essential to notice that the FDA has not reviewed the peptide for human use, and its security has not been tested in large-scale clinical studies. The only long-term trial was discontinued because of a case of fatal myocardial infarction, deemed unrelated to CJC-1295 itself 9.
Claims of dramatic fats loss, large muscle features, or superior sleep from ipamorelin alone are not borne out by high-quality trials. For kids or adults with recognized GH deficiency, standard-of-care therapies—not secretagogues—govern remedy. And for weight loss, ghrelin agonism can enhance appetite, which may counter goals. Sermorelin is a cornerstone of anti-aging therapies as a result of its capacity to raise development hormone (GH) ranges. This increase in GH has transformative effects on the getting older course of, leading to the reduction of wrinkles, enhanced pores and skin elasticity, and an overall enhance in vitality. It empowers individuals to maintain up a youthful look and elevate their quality of life as they age gracefully.
Ultimately, the selection between Sermorelin vs. CJC-1295 is dependent upon your individual health goals, preferences, and price range. Both peptides have been shown to successfully increase HGH ranges and provide numerous well being advantages. Consulting with a healthcare skilled can help you make an knowledgeable choice and ensure that you achieve the very best outcomes from peptide remedy. When considering Sermorelin vs. CJC-1295, it’s essential to consider your specific well being objectives. If you are on the lookout for a quick boost in HGH levels with a well-established security profile, Sermorelin may be the higher choice. However, if you prefer a peptide with a longer period of motion and are willing to watch for potential unwanted facet effects, CJC-1295 might be more appropriate.
Peptide dosing is each an artwork and science; practitioners not often agree on one of the best dose of any specific peptide, even less so when combining a quantity of. If you need to examine every individual compound, the guide to the best longevity peptides details how they work. Epitalon is believed to activate telomerase to extend telomere length while regulating circadian rhythms.
These side effects have a tendency to lessen because the physique adjusts to the remedy. However, in the event that they persist or worsen, remember to search medical consideration. If you’re injecting this drugs yourself, use it exactly as directed by your doctor. Do not use roughly of it, and don’t use it more typically than your doctor ordered. The actual amount of drugs needed has been rigorously labored out. Utilizing too much will improve the risk of unwanted effects, whereas using too little might not enhance the condition.
Since using Ipamorelin and Sermorelin together as a peptide stack stimulates the pituitary gland to extend development hormone manufacturing within the physique, quite a few health advantages are experienced by the top user. The Peptide Report () is a complete resource promoting evidence-based healthcare practices. Whereas the information offered on this website is intended for educational and analysis purposes, you will need to understand the limitations and appropriate use of the content. • The Peptide Report and its linked sources offers information about healthcare interventions, remedies and research procedures. This information consists of any referenced scientific or scientific analysis.
Some research has instructed that it can be beneficial for individuals with sure recurrent brain tumors. Sermorelin is a synthetic type of GHRH, used as a medicine for low hGH ranges. It’s no longer manufactured in the Usa after its maker stopped production, but this medication can be obtained from certain pharmacies that make compounded medicines. As usually is the case with such difficult machines as our our bodies, hGH does not act alone.
This is an important discovering for research targeting models of muscle wasting or sarcopenia. The aim of this https://git.micahmoore.io/tahliapung4556 hormone therapy research is to see if the sermorelin ipamorelin combination can effectively mitigate age-related muscle loss and enhance the upkeep of lean body mass. The ipamorelin peptide’s function in this combination is vital because it offers the selective, highly effective trigger needed to maximize the GH pulse with out introducing catabolic stress hormones. Researchers taking a look at other methods to assist tissue well being often investigate compounds like BPC-157 peptide for tissue restore for comparative data towards these systemic development factor results. It alerts the pituitary gland to release your individual development hormone. That shift can support fat loss, lean muscle mass, skin well being, bone density, and sleep quality over time.
Deeper sleep exhibits up as fewer night awakenings and easier mornings. Your physique releases development hormone in pulses through the day and night time. In preclinical and translational work, ghrelin agonism has demonstrated results on urge for food, gastric motility, and physique weight regulation. Ipamorelin particularly has shown promotility and feeding results in animals and selective GH launch without the ACTH/cortisol rises noted with some older peptides. These findings support ongoing exploration in postoperative ileus, cachexia, and different situations where urge for food and gut motility are impaired.
Deep (slow-wave) sleep aligns with the biggest endogenous GH pulse. Night dosing is usually chosen to “stack” a pharmacologic pulse onto the physiologic peak. Conversely, fragmented sleep, shift work, or untreated sleep apnea can disrupt GH dynamics and limit the impact of secretagogues. Addressing sleep hygiene, circadian regularity, and apnea (if present) usually strikes the needle greater than peptide dosing tweaks. Suppose of ipamorelin as a GH-pulse amplifier with a brief window of action.
Ipamorelin takes the highlight for its role in aiding muscle restoration, stimulating the expansion of latest muscle fibers, and even contributing to faster therapeutic from injuries. Some are like your trusty sidekick, while others is normally a villain in disguise, wreaking havoc on your long-term goals. Today, we’re diving into the realm of Ipamorelin, the expansion hormone-releasing rockstar that’s been making waves. When used correctly, these peptides may be powerful instruments for enhancing performance, restoration, and overall well-being. Ipamorelin works a bit differently by targeting the ghrelin receptor within the pituitary gland. This additionally leads to elevated GH manufacturing but through a unique pathway than Sermorelin.
However, it’s essential to grasp that whereas it will enhance your stage of development hormone, sermorelin therapy just isn’t a quick fix. The remedy works by progressively increasing the discharge of growth hormone, allowing your physique the time it wants to regulate to the increased manufacturing of HGH. Most sufferers expertise refined, progressive modifications over weeks and months as the discharge of growth hormone will increase. Typically, it might possibly take several months for age-related signs to disappear and the full results of sermorelin to turn into obvious, so persistence is important.
Sermorelin is a peptide that resembles development hormone releasing hormone. As A Substitute of direct stimulation of the pituitary gland, Sermorelin acts like the body’s pure GHRH plus promotes normal development hormone production. Finally, there are documented, albeit preliminary, Positive ipamorelin effects on Bone Mineral Density (BMD). The extended and enhanced GH signal from the sermorelin ipamorelin mixture is hypothesized to stimulate osteoblast exercise, the cells answerable for bone formation. We provide high-quality compounds like Thymosin Alpha 1 peptide for immune and bone analysis for those conducting comparative studies on bone well being. A secondary speculation focuses on the Amplified Anabolic and Regenerative cagrilintide benefits. This is tested in fashions of muscle atrophy or wound healing, the place researchers measure outcomes like elevated protein synthesis rates or accelerated closure of epithelial wounds.
If you’re targeted on big lifts, fast bounce-backs after training, and preserving lean muscle, each tesamorelin and sermorelin come up as sturdy choices. Which feels right for you—do you wish to lean down quick or rebuild even quicker? Either method, understanding tesamorelin vs sermorelin means you’re thinking like a critical athlete shaping your personal path. TA1 is believed to be a significant component of Thymosin Fraction 5 liable for the activity of that preparation in repairing immune function. TA1 performs a significant role within the management of immunity, tolerance, and irritation. It manages immune response by way of an preliminary motion on the cells of the innate immune system and this acts as an endogenous regulator of both inflammatory and adaptive immune responses. TA1’s immunomodulatory actions are heart totally on the augmentation of T- cell perform.
Calculating the proper Sermorelin dosage requires consideration of various components and guidelines to tailor the treatment to individual needs. Read our Sermorelin tablets vs. injection guide to find one of the best plan in your health goals. You should begin your peptide therapy with one complement taken on the same time every day. It’s additionally advisable to begin with an eight-week cycle before building as much as a most twelve-week cycle ultimately. Ipamorelin, however, works a bit in a special way and mimics a gastric hormone often known as ghrelin. Ipamorelin binds to ghrelin receptors within the pituitary gland and stimulates HGH from there. In the previously talked about examine by Sigalos et al., both GHRP-2 and GHRP-6 have been administered with sermorelin as a half of a combination GHS regimen (30).
Analysis research have shown promising leads to using HGH secretagogues to doubtlessly improve cardiovascular well being markers such as lipid profile and vascular operate. These studies, carried out over various periods ranging from weeks to months, highlight the significance of long-term security monitoring and cautious assessment of potential side effects. The pores and skin advantages from hormone optimization by way of elevated collagen production, resulting in enhanced elasticity and decreased appearance of wrinkles and fantastic lines. Human development hormone (HGH) secretagogues are recognized to stimulate the production of insulin-like growth issue 1 (IGF-1), a key player in muscle growth and repair. As Quickly As in circulation, progress hormone acts on varied tissues and organs, selling development, regulating metabolism, and aiding in tissue repair. The interaction between peptides and progress hormone is finely tuned, ensuring optimum levels are maintained to help a spread of physiological processes.
Look for sources that provide transparent quality control, third-party testing, and detailed product data. Consulting a healthcare skilled is essential to determine the finest option on your specific wants. Whereas the FDA has banned compounding pharmacies from ensuring peptides, there are different pharmacies—dubbed ‘unregulated pharmacies’—that usually are not regulated by the federal government. These pharmacies should still manufacture banned peptides—but be cautious of quality and security if you’re intent on going this route. For instance, many oral versions of peptides (like BPC-157 and Thymosin Beta 4) are not banned—it’s just the injectables.
Getting probably the most out of Sermorelin isn’t just about utilizing it — it’s about using it correctly. Whether Or Not your goal is to boost recovery, improve fats loss, support anti-aging, or build lean muscle, the best dosage and timing make all of the difference. Sermorelin is likely one of the most generally used growth hormone–releasing peptides, favored for its capability to securely and naturally enhance your body’s personal growth hormone (GH) manufacturing.
After 9 weeks, body weight within the GH-deficient mice elevated by 15.3% in these handled with ipamorelin in comparison with 95.5% in these treated with GH. In non-GH-deficient mice, ipamorelin and GH led to sixteen.9% and 27.5% increases in body weight respectively. The timing of the load acquire differed between agents as ipamorelin only produced weight acquire within the first 1–2 weeks whereas GH-treated mice saw weight gain persistently across the 9 weeks. It is price noting, however, that there have been no adjustments in the relative weight of the dissected organs with ipamorelin whereas GH led to increased liver weight. This suggests that sufferers treated with ipamorelin may not expertise the identical organomegaly as that seen in patients treated with GH itself. Ipamorelin is an artificial pentapeptide that is a selective agonist of the ghrelin/ GHS receptor pathway (54).
The augmented power levels resultant from Sermorelin consumption enable individuals to exhibit improved stamina and endurance levels throughout bodily actions. This attribute proves advantageous for these in search of to reinforce their athletic efficiency or undertake a more lively life-style. It is crucial for individuals using Ipamorelin to acknowledge the potential for hormone imbalances, as this can result in signs corresponding to fatigue, temper swings, and alterations in urge for food. Regular monitoring of hormone levels under the supervision of a healthcare professional is essential to promptly identify and handle any imbalances.
Alongside these shared advantages, sermorelin, ipamorelin, and tesamorelin have unique perks, too. Ipamorelin and CJC 1295 may help you burn fat, recover faster from illness, improve libido, and boost pores and skin elasticity. Without adequate sleep, older adults are extra in danger for falls, memory issues, or depression. Moreover, insufficient sleep can also velocity along the getting older course of. CJC 1295 Ipamorelin and Sermorelin are related of their administration, each require subcutaneous injections. Sermorelin is on the market as an injection, whereas Ipamorelin may be administered orally or subcutaneously. Nonetheless, CJC 1295 Ipamorelin provides you a extra regular increase of GH release.
References:
https://asfuyao.top:8300/jerroldernst22
The following info includes solely the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is completely different, don’t change it except your physician tells you to take action. Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or consuming sure kinds of food since interactions may happen. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines can also trigger interactions to occur.
In Contrast To artificial progress hormone, which directly replaces GH, Sermorelin works by encouraging your physique to supply GH naturally, which results in a more balanced and controlled strategy to hormone optimization. Whereas oral sermorelin remedy is a method of administering the expansion hormone releasing peptide, some parts get misplaced during the digestive course of. They dissolve under the tongue, enabling sermorelin to be absorbed immediately into the bloodstream. This strategy bypasses the gastrointestinal tract and prevents the peptide from being weakened. Side results of sublingual troches may embody mouth irritation, sore throat, or disagreeable taste.
Not only does this assist in shedding extra fats, however it also plays an important role in enhancing overall power levels and vitality, selling a healthier lifestyle. This distinctive blend works by targeting the body’s metabolic price, resulting in increased calorie burn even at rest. Peptides like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin stimulate the discharge of development hormones, which in flip enhance fat breakdown and utilization for vitality production.
But, research has employed sermorelin for investigating its potential in wholesome and GHD adults. The out there information report that sermorelin has been administered in doses starting from 1-2mg/daily, administered as one or two injections per day for up to sixteen weeks 13. Development hormone, also called human development hormone (HGH), is concerned in plenty of organic features including the copy of cells and the repair of tissue 2. As A Result Of GH is so important for the expansion and repair of tissue, there’s currently strong analysis curiosity in the extent to which HGH may improve body composition and efficiency. Usually, the peptide is both administered once day by day before mattress or cut up into 2 – 3 smaller doses spread all through the day. Each approaches to administration could be effective and have been shown to elicit constructive leads to medical studies.
Clinical studies have shown that Sermorelin remedy can lead to increased muscle mass, decreased body fats, improved bone density, and enhanced vitality ranges. Individualized dosing tailored to each patient’s particular needs is important for reaching the desired therapeutic effects. Scientific research have proven that monitoring progress all through the therapy course of is essential for evaluating its total success. Regular assessments help healthcare providers make knowledgeable selections regarding adjustments in dosage and therapy period to optimize results. The increased progress hormone ranges stimulated by Ipamorelin could promote lipolysis (fat breakdown) and metabolic rate elevation, probably making it useful throughout cutting phases.
Healthcare providers play a vital position in monitoring the patient’s response via common check-ups and laboratory exams to assess hormone ranges and total well being status. Proactive management is crucial in the early detection of adverse reactions, permitting for timely interventions. Individuals present process Sermorelin acetate remedy typically report improved sleep high quality, enhanced cognitive operate, and increased vitality levels.
Peptide remedy, with its focused approach and potential advantages, has garnered important curiosity from individuals seeking alternative treatment options. Scientific trials play an important function in validating the efficacy of peptide therapies, guiding healthcare suppliers in recommending probably the most suitable treatment options. When determining the optimum remedy period for the mix, people should steadiness the desire for muscle growth with the sensible features of remedy effectiveness and prices involved. By enhancing protein synthesis and supporting tissue regeneration, the blend accelerates the restoration process after intense exercises.
Based on person expertise, for fitness objectives, you’ll have the ability to inject 200mcg-300mcg of ipamorelin up to 3 occasions a day. For anti-aging purposes, use it as quickly as a day with roughly 200mcg of ipamorelin. The injectable type stays the gold normal, facilitating precise administration and maximizing the potential benefits of this development hormone-releasing peptide. This delays the aging process of a person and makes you look youthful and extra energetic with greater collagen production for glowing pores and skin, more healthy nails, and dense hair. Higher progress hormone (GH) levels due to ipamorelin help in a deep sleep. Sleep-related secretion of GH appears to be primarily depending on the release of growth hormone-releasing hormone.
Weigh the potential advantages in opposition to the potential risks before taking this medication whereas breastfeeding. Though this medication is often well-tolerated, tell your doctor about any allergic reactions, medical conditions, medicines, and dietary supplements you take. The producer stopped making this drug in 2006, and it’s not FDA-approved for this purpose.
References:
https://computerhalle.eu/marcyclarkson
Below is a structured breakdown of tips on how to dose, time, and stack Ipamorelin for finest outcomes, including standalone and combination protocols. This methodology of injection ensures that the blend is delivered directly under the pores and skin, allowing for environment friendly absorption into the bloodstream. Dosage guidelines for the Sermorelin Ipamorelin blend can range depending on particular person wants and well being components, however healthcare providers sometimes recommend starting at a lower dosage and adjusting as wanted. Ipamorelin is classified as a development hormone releasing peptide (GHRP) that simulates the effects of ghrelin by inducing the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. Sermorelin works by mimicking the results of GHRH, which is responsible for stimulating the pituitary gland to provide development hormone.
Whether Or Not you’re recovering from an damage, attempting to regain lean mass after a reduce, or just optimizing restoration between onerous classes, Ipamorelin can offer a natural-feeling performance edge. For greatest outcomes, it can be used as a standalone peptide—or stacked with synergistic compounds like CJC-1295, MK-677, or BPC-157 relying in your objectives. CJC-1295 is a development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) with DAC that extends HGH release to 6-8 days. When mixed with Sermorelin+Ipamorelin, it creates “stacked” results. CJC-1295 provides the inspiration pulse whereas the others improve and delay it. Tesamorelin is FDA-approved for HIV-related fats loss but causes more hunger. Ipamorelin offers the cleanest release with minimal unwanted aspect effects.
This peptide hormone is produced within the pituitary gland of your brain. A peptide stack is the intentional mixture of two or extra peptides, chosen so their actions complement one another. Clever peptide stacks produce effects higher than the sum of their individual benefits. They tackle the body’s interconnected systems (ie hormones affect sleep, sleep affects metabolism, and metabolism impacts inflammation). Small proof-of-concept trials evaluated intravenous ipamorelin for postoperative ileus after bowel surgical procedure. Pharmacokinetic studies in wholesome volunteers mapped dose–response relationships for GH release and confirmed the temporary, pulse-like impact.
Ipamorelin is not an FDA-approved remedy for anti-aging, efficiency, or general wellness. In many international locations it sits in a gray zone the place research use could additionally be permitted however business marketing is restricted. Compounding or internet sales don’t guarantee high quality, sterility, right id, or authorized compliance. If a clinician proposes ipamorelin, ask about precise sourcing, batch testing, documentation, and monitoring plans—including IGF-1 targets and glucose surveillance.
Nonetheless, definitive research to assist the anti-aging effect of sermorelin https://git.sebastianfisahn.com/linnoble102361 missing. The use of sermorelin in healthy adults to reverse the consequences of growing older and in bodybuilding remains controversial. Some peptide enthusiasts look to nootropic stacks—combining peptides focusing on mind well being, neurotrophic signaling, or mitochondrial help. For example, some longevity guides include stacks combining peptides (like NAD+, Semax, Dihexa) for brain clarity, neuroplasticity, and anti-aging.
For bodybuilding, Sermorelin+Ipamorelin beats Tesamorelin as a outcome of higher anabolic results. Sermorelin supplies sturdy preliminary HGH pulses while Ipamorelin extends the discharge window. Together they create sustained growth hormone elevation all through the day. Most users report better outcomes than both peptide alone. Understanding the correct dosage and reconstitution process is crucial for attaining the desired therapeutic outcomes. In this weblog post, we’ll present an easy-to-use Sermorelin reconstitution calculator and dosage chart, designed to simplify your calculations, and ensure correct dosing.
Progress hormone is naturally produced by the pituitary gland and is critical for development in kids. In children who fail to develop normally as a end result of their bodies aren’t producing sufficient progress hormone, this medicine may be used to increase the amount of progress hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Peptides used in stacks may help fat loss by boosting lipolysis (fat breakdown), improving insulin sensitivity, preserving lean mass, and optimizing metabolism. Advantages of fat burning, preserving lean muscle, and regulating appetite are anecdotal. Weight Problems and insulin resistance blunt both basal GH secretion and secretagogue responses.
Analysis exhibits these peptides improve IGF-1 levels 300% larger than either peptide alone. A 2006 research published within the Journal of Scientific Endocrinology found CJC-1295 considerably extended GH launch period. This medicine aims to imitate your body&aos;s natural rhythms and processes as carefully as potential. An correct dose ensures your body receives the right alerts, promoting optimum health and well-being with out overburdening your system.
By naturally stimulating the manufacturing of growth hormone, Sermorelin helps enhance a spread of bodily functions, including cellular regeneration, metabolism, and overall vitality. This makes it an excellent alternative to synthetic HGH, because it reduces the chance of imbalanced hormone ranges. HGH Peptide Therapy refers to treating the body with peptides by injection or oral/topical administration.
Rather than administering HGH directly, researchers can use sermorelin to increase HGH levels in test subjects by naturally stimulating the pituitary gland to release extra endogenous HGH. As A Substitute of spiking HGH to supraphysiological levels, sermorelin is believed to supply a gradual enhance in HGH in a stable, predictable method. Many patients will discover some significant increases in modifications in the body after the first month. The full advantages are normally absolutely observed after three to 6 months of therapy. Three months in a row is a regular protocol with 1-2 weeks off earlier than beginning another 3 months of therapy. Sermorelin is peptide similar to GHRH (a growth hormone-releasing hormone) and binds to the GHRH receptor. This stimulates and prolongs the manufacturing of growth hormones while maintaining the pure ebb and circulate of how your body operates.
Nonetheless, the producer of sermorelin determined that it required greater doses to be efficient in kids and that it was not as efficient as various treatments. Cognitive peptides sometimes require shorter cycles (4-6 weeks) with equal rest durations to maintain effectiveness. Diminishing returns typically occur when receptors become downregulated or desensitized. This usually happens between 8-16 weeks relying on the peptide mixture and particular person response patterns. The stack provides calm focus, enhanced learning, and emotional stability inside 1-2 weeks, with sturdy nootropic effects rising at 4-6 weeks. You’ll walk away with newbie stacks, superior combos, security logic, widespread stack dosages, and how to do it the right method.
Dr. Camp underscores that in distinction to artificial hormones, Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin prompt the body’s intrinsic production of development hormone, leading to more enduring and harmonized hormone ranges. This strategy not only diminishes the likelihood of opposed effects but in addition bolsters the body’s pure mechanisms, fostering extended health advantages for sufferers present process hormone therapy. Low progress hormone levels often trigger lack of muscle mass and strength, weaker bones, lowered train capacity, elevated body fats, decreased stamina, poor restoration, and non-restorative sleep. Certainly, aging-related decline in development hormone levels is answerable for many of the debilitating effects commonly skilled when getting older. This method of injection ensures that the blend is delivered directly underneath the pores and skin, allowing for efficient absorption into the bloodstream.
Yes, many individuals report improved sleep quality whereas utilizing Ipamorelin. It can promote deeper, extra restorative sleep by naturally boosting progress hormone launch at night, which performs a role within the body’s restoration https://gogs.bardels.me/michellfredric restore processes. From Dr. Camp’s perspective, the utilization of Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin represents a notable development in progress hormone therapy, offering a safer and extra organic technique for hormone alternative. These peptides have exhibited encouraging outcomes in augmenting muscle mass, bone density, and general high quality of life for individuals experiencing hormone deficiencies.
Prompt reporting of any adverse effects permits patients to contribute to the continuous monitoring and analysis of drug safety. The establishment of an everyday routine has a profound impact on the effectiveness of the therapy routine. Along with adhering to treatment pointers, it is essential to concentrate on dietary choices and physical activity ranges. A well-balanced diet, replete with important vitamins, and a consistent train regimen can complement the therapy process, amplifying its therapeutic benefits. Monitoring personal well-being and noting any adjustments in symptoms are important in facilitating dialogue with healthcare professionals to fine-tune treatment protocols as needed.
Watch for signs of carpal tunnel like hand tingling, persistent edema, or headaches that do not settle. People with lively cancer, severe sleep apnea, or uncontrolled cardiovascular disease need careful supervision. Over months, many people report steadier joints and fewer aches after hard periods. Ipamorelin is on the market as a lyophilized powder that should be reconstituted into liquid kind after which administered through injections to make sure sufficient bioavailability.
Sourced from trusted and respected peptide sciences, all of our merchandise bear rigorous testing to ensure the very best ranges of purity, efficiency, and effectiveness. Whether you’re focused on muscle development, fat loss, or anti-aging, we attempt to offer superior options that empower you to realize your wellness aims with confidence and ease. Determining the appropriate dosage of the Sermorelin Ipamorelin blend is important to make sure each security and efficacy. This process sometimes necessitates consultation with healthcare professionals so as to establish a customized care plan. Various components come into play when making dosage choices, including the individual’s age, weight, general well being status, and particular medical conditions. For most patients who’ve been identified with age-related progress hormone loss, sermorelin therapy can have remarkable advantages. The medical capability of sermorelin to lift progress hormone levels has been properly documented in the medical literature.
This is very true for researchers with expertise handling Ipamorelin and other peptides. In our experience, the 2 following vendors are trusted sources of ipamorelin and different research peptides. A Number Of peptide vendors inventory research-grade ipamorelin for buy by certified researchers and laboratory professionals. Some researchers have theorized that this mix treatment may be particularly helpful in managing the signs and signs of growing older, in addition to aiding in the reduction of inflammatory situations. As previously acknowledged, ipamorelin particularly stimulates GH without activating other hormones, thereby lowering the chance of negative unwanted effects. The solely published trial information (Beck et al.) examined the use of ipamorelin for a really brief period of time (7 days) and little is known about the long-term results of this peptide. Researchers thinking about exploring the effects of ipamorelin will note that this analysis chemical has no formally accredited dosage.
This information consists of any referenced scientific or medical analysis. The Peptide Report makes no claims about how the motion or treatment offered can treatment, deal with or stop any medical situations or ailments. • The Peptide Report upholds the best research integrity, requirements, and ethical conduct. All research referenced on this web site complies with national and worldwide rules and pointers for scientific trial data.
This makes it a most well-liked choice for patients looking for a extra physiologically balanced, regulated strategy to enhancing GH levels. Sermorelin stimulates your pituitary gland to release your own growth hormone. Sermorelin retains feedback control and helps pure production. If you need actual changes in power, restoration, sleep, and physique composition, sermorelin could help. Many adults ask if sermorelin can ship these results with out the risks of direct HGH therapy. This guide shows what to expect before and after sermorelin therapy, the means it works inside the pituitary gland, and how to stack it with a healthy way of life for best outcomes.
Banned-substance lists are updated annually; ipamorelin has been specifically named among prohibited development hormone secretagogues, and violations can carry multiyear sanctions. Because ipamorelin reliably increases GH (and usually IGF-1 downstream), it may affect lean mass accrual, restoration from catabolic stress, bone turnover, sleep structure, and urge for food. The quick half-life and receptor selectivity additionally make it an appealing device to study GH pulses with out chronically elevating cortisol or prolactin.
More specifically, they each seem to upregulate the production of growth hormone. The progress hormone appears to play a vital role in accelerating progress and is considered to operate primarily to manage metabolic functions. Each Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin offer unique benefits relying in your objectives.
Moreover, Dr. Camp underscores the importance of constant monitoring all through the treatment process to change dosages as required for optimal outcomes. Through meticulous monitoring of affected person advancement and applicable dosage modifications, Dr. Camp is confident that patients can attain probably the most favorable results with development hormone remedy. To handle redness or swelling on the injection site, the appliance of a cold compress can help in reducing irritation. Sufficient hydration earlier than and after administering injections might help alleviate complications and fatigue. Patients are advised to promptly report any persistent or severe unwanted effects to their healthcare provider for steering on appropriate measures or adjustments in dosage.
Bounce into the science behind how this combo works to enhance progress hormone secretion, shield your nervous system, and potentially flip again the clock on getting older. Whether you’re looking to boost your restoration or perceive the most recent in anti-aging analysis, the Sermorelin Ipamorelin stack is a captivating matter you won’t want to miss. This combination can boost muscle development, enhance weight reduction, and combat symptoms of cognitive decline similar to memory lapses. “Administration of recombinant human progress hormone (rhGH) in weight problems has been recognized to lead to a lower in visceral adiposity and a rise in lean physique mass. Your nutrition, sleep habits, train routine, and stress levels can have an result on progress hormone manufacturing (GH is of course launched in pulses each 3-5 hours or so).
Conversely, Ipamorelin serves as a selective progress hormone secretagogue, leading to a extra measured and prolonged launch of growth hormone. Choosing a good development hormone therapy requires several particular factors plus your targets, age together with general well being. If you know how sermorelin and ipamorelin work, you’ll make a higher choice for your needs. A typical ipamorelin dosage ranges from 200 to 300 micrograms per day, administered via a subcutaneous injection. Dosage can range relying on your targets, age, and hormone ranges, so it’s best to work with a healthcare supplier to determine the right quantity for you. Potential side effects of Sermorelin embrace mild headaches, nausea, and minor reactions at the injection site. Sermorelin capabilities by stimulating the manufacturing of progress hormones in the body, which could find yourself in hormone stage fluctuations, probably resulting in complications and nausea.
It’s a combination that taps into your body’s innate hormonal intelligence, instead of overriding it like traditional hormone substitute therapies. Their individualized strategy and cutting-edge treatments have revitalized my life. The staff’s dedication to my health has been unparalleled, making this a fantastic expertise total. In Ny, the place outdoor activities, gyms, and health tradition thrive, sustaining a wholesome way of life alongside this combination therapy is essential to staying sturdy, energized, and motivated. I really have a theory that the MOTS-c might be simpler at boosting NAD+ ranges. High levels of this peptide are found in the younger and in very lean individuals.
At AlphaMD, we imagine in offering evidence-based, patient-centered care for those exploring TRT and peptide therapies. Our skilled medical group provides personalized consultations to help decide whether Sermorelin or different therapies are the proper fit for you. If you’re considering Sermorelin and need professional steering, our on-line telehealth services make it easy to get started—all from the consolation of your own home. To start, clear the injection site totally with an alcohol swab to scale back the chance of an infection. Next, using a skinny needle (commonly gauge), pinch the skin between two fingers to create a small mound for injection.
Common unwanted aspect effects of peptide mixtures could embody pores and skin irritation on the injection web site, gentle headaches, or nausea. It is critical for individuals to engage in consultations with a healthcare skilled before commencing any peptide regimen to judge potential risks and establish the appropriate dosage. Enough monitoring and supervision throughout the process are essential to ensure the secure and effective utilization of peptides. Elements similar to underlying health situations, allergy symptoms, and drugs interactions ought to be meticulously assessed to forestall opposed reactions.
References:
https://rjlove.org/@fanniekillian3
Tesamorelin and Sermorelin act on the GHRH receptor, whereas Ipamorelin targets the ghrelin or progress hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R). Ipamorelin is a synthetic peptide focusing on the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor, stimulating the release of GH immediately from the pituitary gland. Sermorelin may mimic the body’s natural “pulsatile” release of progress hormone (9).
On the opposite hand, Ipamorelin is considered a safer choice, providing a extra managed release of HGH with no impression on cortisol and prolactin ranges. If you’re looking to use the peptides Hexarelin and Ipamorelin via subcutaneous injection, their dosing protocols can be found under. You may not feel as hungry or bloated, however complications, dizziness, and a response at the site of injection have been reported (although these not often happen in experienced users). Acting as functional somatostatin antagonists, GH secretagogues potentiate the actions of GHRH on GH secretion, enhancing pulsatile GH secretion.
This means it could improve GH levels with out disrupting the fragile balance of the endocrine system, potentially leading to fewer unwanted side effects compared to exogenous GH therapy. These unwanted side effects, though usually momentary, can embrace redness, pain, or swelling at the injection site. It’s important for people receiving these peptides to observe and report any persistent or severe reactions to their healthcare suppliers. When evaluating Sermorelin and CJC-1295, it is important to think about components corresponding to their progress hormone release mechanisms, effectiveness in hormone optimization, and potential side effects. While Sermorelin usually has mild unwanted facet effects, some users report localized irritation or delicate dizziness.
That alone units it aside in a field the place many peptides exist in regulatory grey areas. Visceral fat is the deep belly fat that’s usually proof against food plan and train. In this blog, we shall be introduced to Tesamorelin and IGF1- LR3, two peptides with distinct makes use of in medication. We will talk about their differences and similarities in addition to separate features. Tesamorelin vs. CJC-1295CJC-1295 (with DAC) provides sustained GH launch over 24 hours, whereas Tesamorelin’s action peaks rapidly and then declines; for fast metabolic shifts, Tesamorelin is usually favored.
This technique includes fine-tuning dosages and monitoring responses intently to avoid overstimulation. Shut coordination with medical groups helps guide secure and efficient testing of this combination. Yes, Sermorelin has been reported to improve sleep high quality by promoting deeper, more restorative sleep, which is essential for total health and recovery. Sermorelin usually requires day by day or near-daily injections as a result of its shorter half-life, permitting for consistent development hormone launch. Some people choose to combine the 2 to assist each fat loss and muscle recovery. Tesamorelin is extra targeted for fat loss in the midsection, while ipamorelin is great for people who need total help with energy, restoration, and longevity. Tesamorelin is a kind of peptide known as a GHRH analog, which implies it helps your mind launch extra of your personal human development hormone.
Many bodybuilders utilizing tesamorelin for fast fats loss or muscle positive aspects report extra swelling and stiffness after heavy lifting days. These results usually occur because tesamorelin makes your body push out more growth hormone in a quick time. Tesamorelin and sermorelin each act as progress hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) analogs.
It also can trigger important side effects as a result of growing prolactin and cortisol. Here’s a quick look at the most effective development hormone peptides and what they’re typically paired with. A healthcare professional ought to know these security elements about ipamorelin vs sermorelin. It usually just causes a small pores and skin bump, some delicate redness, or a bit of heat right where you give the shot. Most individuals using sermorelin for muscle recovery, deeper sleep, or sluggish positive aspects share that these unwanted side effects go away fast or never bother them at all. In clinics, you’ll see it help youngsters develop taller and adults feel higher, stronger, and extra recovered.
As you’ll see in the subsequent benefit, there’s another method during which Tesamorelin could be assist improve your cardiovascular health. People with NAFLD usually suffer from liver fibrosis, or scar tissue, which might impede liver operate and lead to liver failure. As you’ll see later, Tesamorelin’s mechanism of motion is similar to that of Ipamorelin. So https://gitea.potatox.net/phillisylx5664 we’ve in effect is a GHRH analog that is extra metabolically secure and potent than naturally-produced GHRH itself.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that both peptides are generally well-tolerated, with few antagonistic effects reported. Nevertheless, individual responses to treatment could vary, and unwanted aspect effects such as injection website reactions, headache, and gastrointestinal symptoms have been reported with each Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin. Finally, the selection between Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin will depend on components corresponding to the precise indication for therapy, patient preferences, and individual response to remedy. This makes sense when you suppose about that increasing progress hormone production results in increased muscle mass, a phenomenon well-established by scientists for many years. Sermorelin’s influence on development hormone levels enhances the synthesis of collagen. This enhance in collagen manufacturing is especially noteworthy and diminishes with age.
By working within the bypass move or on a free-standing tank, the Desorber-Filter-Unit D10 ensures steady oil drying and fine filtration, independent of machine operation. The desorption course of works independently of viscosity, components and air content material within the oil. CJC® Fantastic Filters are offline oil filtration options with integrated circulating pumps for off-line set up. The filters are recognized all over the world as highly environment friendly purification systems for applications involving hydraulic oil, lubrication oil, gear oil, diesel gas, quenching oil, phosphate esters and more. By investing in our oil filtration techniques, you will obtain the lowest value per kilo of dust removed and significant price savings, with each short- and long-term advantages. For example, your in-line oil filters and components could have longer lifetimes. You will avoid lots of the oil-related failures and breakdowns caused by contaminated oil.
We are dedicated to holding the best standard for public safety to achieve a county freed from crime and public disorder. The CJC additionally has jurisdiction to investigate allegations that a decide has a physical or mental incapacity which impacts the judge’s efficiency. You could both fill in and fax the CJC’s downloadable grievance form or fax a letter to the CJC describing your complaint. If you wish to remain anonymous, do not provide any personal or contact information. On the grievance form or in your letter, explain, in your personal words and with as a lot detail as potential, the circumstances that led to your complaint and the information and evidence that you consider exist to support your grievance.
Our mission is to provide the residents of El Paso County efficient and environment friendly public safety services. CJC® Fantastic Filters are perfect for controlling oil contamination levels for particles, water, and degradation products similar to oxidation resin/sludge and varnish. Research exhibits that 80% of oil associated failures and breakdowns are caused by contaminated oil! Preventive oil upkeep is subsequently an important factor to ensure optimum gear reliability and avoid system breakdown. Curry’s third album, Simplicity, was launched in 1981, again by A&M Information.41 This report, which did not promote in addition to the earlier offerings, mixed each original songs and cover variations. One of Curry’s best-known television roles is as Pennywise the Clown within the horror miniseries Stephen King’s It (1990).
With CJC® Offline Oil Filters put in, you guarantee steady clean and dry oil, increased uptime, extended part and oil lifetime, leading to financial savings in your maintenance prices. All of which results in lowered environmental impression because of many litres of waste oil saved every year. Particles, water, oil degradation merchandise (Varnish, oxidation residues, and so on.) and acids in the oil?
CJC Filter Separators combine fine and depth filtration with coalescing filtration for separation of free water from oil and diesel. Simultaneously, CJC Filter Separators take away particles, oil ageing products and acid compounds from oil and diesel. CJC Filter Separators are perfect for the use in the industrial, vitality, mining as nicely as marine and offshore sector.
Apart from one Fangoria interview in 1990, Curry by no means publicly acknowledged his involvement in It until an interview with Moviefone in 2015, where he called the position of Pennywise “a beautiful part”. He rose to prominence as Dr. Frank-N-Furter in the musical movie The Rocky Horror Picture Show (1975), reprising the role he had originated within the 1973 London, 1974 Los Angeles, and 1975 Broadway musical stage productions of The Rocky Horror Show. Grant Thornton LLP is a licensed independent CPA agency that provides attest companies to its clients, and Grant Thornton Advisors LLC and its subsidiary entities provide tax and business consulting providers to their shoppers. Grant Thornton Advisors LLC and its subsidiary entities usually are not licensed CPA firms. If you consider that a judge has a incapacity affecting his or her efficiency or has violated one or more of the Canons of the Code of Judicial Conduct, it’s applicable to file a criticism with the CJC. Please describe as particularly as potential what the choose did or stated that causes you to imagine he or she has a disability or has dedicated misconduct.
Please be inspired from our video assortment with installation guides, tips on how to substitute CJC® Filter Inserts, oil situation monitoring etc. and find out how straightforward oil maintenance could be for you with CJC® – your pure solution for optimum oil upkeep. Director Ridley Scott solid Curry in the film after watching him in Rocky Horror, thinking he was best to play the function of Darkness. It took 5 and a half hours to apply the make-up wanted for Darkness onto Curry and on the end of the day, he would spend an hour in a shower in order to liquefy the soluble spirit gum.
The modular filter units may be customized to particular customer necessities, whether or not the oil quantity is 2 litres or 200,000 litres. Production that makes use of CJC® Nice Filters will experience decrease price of operation due to a lowered want for maintenance as well as extending part lifetime. Notably in the paper, metal, plastics and metal processing industries, in addition to in maritime purposes, there’s a high threat of water entering the oil techniques because of the surroundings and processes concerned. Grant Thornton Advisors LLC may use assets from its subsidiaries and domestic and/or international affiliates through the course of providing professional companies to its shoppers. The CJC® Offline Oil Filtration system is an unbiased unit run by a motor, a pump, and an oil filter, reliable for guaranteeing the longevity of applications utilizing oil. Whether Or Not acute or steady water ingress — we offer you the solution that is precisely tailor-made to your application and removes dissolved and emulsified water out of your lubricant. Our fluid consultants can even advise you on advanced issues — all the time with a concentrate on feasibility and cost-effectiveness.
The oil filtration system repeatedly cleans the oil throughout operation, removing damaging wear particles within the system. The fluids are drawn from the unit’s lowest level within the oil reservoir, through the oil filter by a pump, and returned clear to the supply. Oil sensors for the web situation monitoring of oils and fluids, which give you actual actual time knowledge about the oil situation and thus in regards to the machine condition – anytime and anywhere.
Use the “Particular Facts” section of the form to elucidate, in your own words and with as a lot element as potential, the circumstances that led to your criticism and the information and evidence that you simply believe exist to help your complaint. CJC® Depth Filters have a filtration diploma of 3 microns absolute and a really large dirt-holding capability, offering maximum protection. Right Here, you’ll uncover a profession that gives you extra flexibility, opportunity and help to empower your passions.
References:
https://virasocia.ca/read-blog/770_ipamorelin-vs-sermorelin-benefits-dosage-amp-blends-for-bodybuilders.html
All research referenced on this web site complies with nationwide and international regulations and guidelines for scientific trial data. The Peptide Report is devoted to the well timed disclosure of the design and outcomes of interventional medical research, guaranteeing transparency and accessibility. • The Peptide Report research findings shouldn’t be interpreted as conclusive or definitive. The Peptide Report encourages important evaluation and further investigation of the offered info. • Individuals in search of medical recommendation or remedy for any condition ought to avoid utilizing The Peptide Report as an different to professional medical consultation. It is advisable to seek the advice of with qualified healthcare suppliers for personalised medical advice and remedy. Optimizing hormone levels can have a profound influence on various elements of health, together with vitality levels, muscle mass, metabolism, and even psychological clarity.
By sustaining stable GH levels, these peptides may supply protective results towards age-related decline. At Infinity Functional Performance, we prioritize affected person security and results. Our peptides are sourced exclusively from FDA-regulated pharmacies, and coverings are custom-made to individual wants.
It’s essential for individuals receiving these peptides to watch and report any persistent or extreme reactions to their healthcare suppliers. While each Sermorelin and CJC-1295 are synthetic peptides that stimulate the pituitary gland to produce and launch more development hormone, there are some variations in their mechanisms of action. Sermorelin acts on the pituitary gland by enhancing the discharge of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), which in turn stimulates the manufacturing of progress hormone in the physique. Additionally, it is favored by athletes and health fanatics for its potential to reinforce muscle growth, accelerate fat loss, and enhance restoration. CJC 1295, an artificial peptide, has garnered vital consideration for its ability to stimulate the manufacturing of human growth hormone (HGH).
Nonetheless, CJC 1295 Ipamorelin provides you a extra steady increase of GH release. However, diet and stress can inhibit releases and scale back its plentiful benefits. It helps stability the highs and lows all through the day, making a more natural ebb and move.
As a synthetic peptide analog of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), CJC 1295 mimics the results of pure GHRH. It binds to particular receptors on the pituitary gland, prompting the gland to supply and release HGH. However, its effectiveness compared to other choices needs further analysis. Legal alternatives for enhancing performance exist, such as Sermorelin remedy.
The stimulus to the muscle for adaptation is offered by progressive resistance training, GH and IGF-1 will amplify this. Protein is also an important source of constructing supplies for synthesis of latest tissue. When you get good sleep your body has an easier time releasing GH and recovering. Cortisol won’t interfere with the anabolic process if stress is kept to a minimum. Purity is important for security and effectiveness, underdosed and subadulterated formulas might cut back results or trigger potential hurt. While GH can potentially promote the growth of cancers, there is currently no evidence that analysis doses of CJC 1295 DAC leads to most cancers. However patients who are being handled for cancer, or who have a history of cancer, should not take GHSs or first consult their oncologists.
Incorporating these choices could be useful for improving efficiency with out resorting to HGH. Nevertheless, it’s essential to note that both GHRP-6 and HGH can have potential unwanted facet effects, including water retention and joint ache. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to discover out the suitable dosage and monitor any potential side effects when using GHRP-6 or HGH. It works by stimulating the pituitary gland to release more growth hormone, which finally ends up in these constructive results.
Uncover how caffeine impacts weight reduction and why it should not be relied on as a major technique. Learn about healthier alternate options, including way of life changes and GLP-1 medicines, for sustainable weight administration. To discover out if this system is best for you, just answer a quantity of questions about your signs and medical historical past. Your provider will order lab work for you to determine if you’re eligible for therapy with sermorelin or other hormone help throughout your scheduled appointment.
If the water within the syringe becomes cloudy after mixing, that signifies possible compatibility issues. Combining both permits for acute therapeutic results from injectables with baseline support from oral varieties. Peptides work through specific receptor mechanisms while small molecules like NAD+ precursors, resveratrol, or nootropics goal different cellular pathways. As far as I can tell, listed below are the most well-liked doses for each peptide in every stack.
References:
https://gitea.b54.co/susanne3677455
what are the different types of steroids
References:
https://ueno-test.sakura.ne.jp/bbs1/light.cgi?res=2552
cutting agent bodybuilding
References:
https://pestcontrolbatam.com/cara-efektif-membasmi-tikus-di-rumah-dan-gudang-anda/
steroids symptoms
References:
http://forum.myjane.ru/weblog.php?w=10284&previous=10&month=9&year=2024
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Nice blog right here! Also your site quite a bit up fast! What web host are you the usage of? Can I get your associate hyperlink on your host? I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
man on steroids
References:
https://www.merlmerl.com/@zulmabarreiro?page=about
how to get a doctor to prescribe steroids
References:
https://music.white-pilled.tv/beatriz54e6522
Hello, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam comments? If so how do you stop it, any plugin or anything you can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any support is very much appreciated.
muscle works supplements
References:
https://1ajobs.ch/employer/winstrol-vs.-dianabol:-which-is-ideal-for-new-users/?/
long-term exposure to steroids can result in
References:
https://qny.me/nikirawls60203
how to buy steroids online
References:
https://dev-members.writeappreviews.com/employer/five-proven-dianabol-stack-combinations-for-maximum-muscle-gain/
best legal steroid stack
References:
https://ninula.com/employer/dianabol-vs-winstrol-unpacking-the-battle-for-muscle-gains/
how bad are steroids
References:
https://www.google.mn/url?q=https://pedselite.com/terapia-post-ciclo-con-dianabol-dosaggio-durata-del-ciclo-ecc/43822/
are steroids illegal for personal use
References:
http://pattern-wiki.win/index.php?title=martensenjohnson5662
crazy mass results
References:
http://volleypedia.org/index.php?qa=account&state=profile-saved
steroid medicine side effects
References:
https://www.google.com.om/url?q=https://pedselite.com/what-is-anapolon-and-how-does-it-help-in-gaining-muscles/85047/
effects of prolonged steroid use on the human body
References:
https://images.google.bi/url?q=https://pedselite.com/crazy-bulk-anvarol-anavar-paravar-reviews/30277/
what does steroids look like
References:
http://shenasname.ir/ask/user/platejury3
best natural anabolic supplements
References:
https://images.google.com.na/url?q=https://pedselite.com/acheter-les-meilleurs-comprimes-et-pilules-de-dianabol-comment-trouver-les-meilleures-marques-de-dbol/41484/
beginner steroid stack
References:
https://md.un-hack-bar.de/DSYc57w_TdiZ5wyixunu1Q/
how to take anadrol properly
References:
https://freebookmarkstore.win/story.php?title=world-anti-doping-agency%E2%80%99s-restricted-substance-catalogue
natural vs steroids pictures
References:
https://output.jsbin.com/vuwopepago/
best steroid cycle
References:
https://molchanovonews.ru/user/heliumsinger59/
Wow! Thank you! I always needed to write on my site something like that. Can I implement a part of your post to my site?
Ремесло – это когда вы создаёте не для соцсетей, а для души https://artisanalcrafts.ru/
is hgh better than testosterone
References:
does hgh increase testosterone (http://lideritv.ge/user/femaleinput35/)
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
hgh bodybuilding nebenwirkungen
References:
how many iu of hgh does the body produce; https://support.mikrodev.com/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=nationjune33,
hgh stack cycle
References:
hgh x2 avis, https://hedgedoc.eclair.ec-lyon.fr/NlQYyUggRJmU9xqmiQamoA/,
hgh dosage iu bodybuilding
References:
best hgh dosage for bodybuilding, https://topspots.cloud/item/413399,
before after hgh
References:
2 iu hgh fettverbrennung [https://langhoff-alexander.blogbright.net/anavar-earlier-than-and-after-muscle-achieve-or-weight-loss]
hgh injections side effects
References:
hgh 3 iu per day results (http://shenasname.ir/ask/user/nestsea32)
hgh cycle dosage bodybuilding
References:
Hgh Frauen Bodybuilding; https://writeablog.net/quiltplate07/anavar-results-and-before-and-after-photos-movies,
does hgh raise testosterone
References:
hgh 2iu per day (https://travelersqa.com/user/altosilica44)
bulking stack steroids
References:
https://newssignet.top/item/446390
steroid side effects for females
References:
https://pad.fs.lmu.de/SxzyyJlPT2CBapsAibWL_g/
anabolic steroid online shop
References:
https://noticias-sociales.site/item/445685
hgh dosage iu
References:
hgh bodybuilding benefits (http://twitter.com/home?status=http://xurl.es/3wttg)
are steroids drugs
References:
https://www.demilked.com/author/plierangora88/
is it safe to order steroids online
References:
https://monjournal.top/item/326353
steroid free bodybuilding
References:
http://mcforces.ru/user/spacepot24/
how many iu hgh for bodybuilding
References:
hgh booster supplement (https://intensedebate.com/people/courtuganda56)
2 iu hgh per day results bodybuilding
References:
dosage hgh bodybuilding (https://musicvideo80.com/user/trailberry42/)
steroids that get you ripped
References:
https://my.vipaist.ru/user/steelbank6/
best place to buy steroids 2015
References:
https://urlscan.io/result/0198bd12-7968-74cc-8d98-aaafb506fed4/
does skipping increase hgh
References:
long term side effects of hgh (https://hangoutshelp.net/user/nursefired92)
hgh 3 iu per day results
References:
hgh dosierung anti-aging [https://baby-newlife.ru/user/profile/307691]
hgh & testosterone
References:
4iu hgh results (http://support.roombird.ru/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=paulflute82)
hgh wieviel einheiten
References:
hgh legal kaufen – http://www.ecccnet.com/forums/users/baitband77/,
recommended dosage of hgh for bodybuilding
References:
hgh ciclo (https://motionentrance.edu.np/profile/greecebakery47/)
hgh and testosterone stack dosage
References:
hgh cycle for beginners – https://a-taxi.com.ua/user/sizefrench0/,
hgh beginner cycle
References:
Ab Wann Wirkt Hgh; https://gamesgrom.com/user/chordharp6/,
hgh anti-aging dosierung
References:
hgh cycle results (http://qa.doujiju.com/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=peafine8)
wachstumshormone hgh vorher nachher
References:
hgh dosage bodybuilding (https://md.entropia.de/3nLpA6asR3iBs6ddR8901A/)
hgh kur dosierung
References:
Hgh hormone bodybuilding (https://prpack.ru/user/timerseal68/)
hgh vorher nachher
References:
dosage of hgh for bodybuilding (http://lideritv.ge/user/cymbalmallet59/)
how many iu of hgh per day for muscle growth
References:
hgh kur, https://bestbizportal.com/read-blog/178698,
how many iu hgh for bodybuilding
References:
Gesicht hgh vorher nachher (https://avtovoprosi.ru/user/whalefrench1)
hgh injecteren
References:
hgh and test cycle (https://diego-maradona.com.az/user/coverpuppy03/)
best hgh booster
References:
hgh Beginner cycle (https://www.hulkshare.com/soyfelony4/)
is hgh harmful
References:
hgh Dosage for injury recovery (https://www.generation-n.at/forums/users/kittenvinyl3/)
does hgh raise testosterone
References:
ciclo Hgh (https://oren-expo.ru/user/profile/608286)
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web savvy so I’m not 100 sure. Any tips or advice would be greatly appreciated. Appreciate it
I really like your writing style, fantastic information, regards for posting :D. “I hate mankind, for I think myself one of the best of them, and I know how bad I am.” by Joseph Baretti.
There are some attention-grabbing points in time in this article however I don’t know if I see all of them center to heart. There is some validity however I will take hold opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we wish more! Added to FeedBurner as effectively
Hello. impressive job. I did not expect this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
Great web site. Lots of useful information here. I?¦m sending it to a few pals ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks in your sweat!
hgh cycle dosage
References:
Testosterone vs hgh bodybuilding; https://webzine.unitedfashionforpeace.com/author/partbead27/,
how many hgh injections should i take
References:
hgh And testosterone; https://www.pinterest.com/eyechange49/,
hgh cycle dosage bodybuilding
References:
hgh Bodybuilding benefits (https://www.shebanglinux.com/members/dinnergrass58/activity/12625/)
4 iu hgh per day results
References:
hgh x2 reviews (https://matkafasi.com/user/courtbead22)
how long to take hgh for bodybuilding
References:
How Many Iu Hgh For Bodybuilding (https://pads.jeito.nl/Mdjxig-fSe-lLOMYOmQUTg/)
testosterone vs hgh bodybuilding
References:
Hgh and testosterone cycle results (https://md.entropia.de/_R8ZAwySR3OXpfXTvJwLBQ/)
hgh results pictures
References:
hgh and testosterone for bodybuilding (http://qa.doujiju.com/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=islandview92)
hgh frauen bodybuilding
References:
How much iu of hgh should i take a day [https://may22.ru/user/weightswan05/]
Hiya! I just would like to give an enormous thumbs up for the nice info you’ve got here on this post. I will be coming again to your weblog for more soon.
hgh bodybuilding cycle
References:
is hgh The Same as testosterone; http://masjidwasl.com/members/limitkiss52/activity/164902/,
Hey very nice web site!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds also…I’m happy to find so many useful info here in the post, we need develop more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
hgh cycles for beginners
References:
http://shenasname.ir/ask/user/roomcarbon0
747liveapk? Sweet, an app! Makes things easier for mobile users. Gotta check it out on the go. Mobile accessibility is a definite plus. 747liveapk
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
You must take part in a contest for top-of-the-line blogs on the web. I’ll advocate this site!
propecia https://bswfinasteride.xyz/# BswFinasteride
craps for dummies
References:
http://engawa.kakaku.com/jump/?url=https://www.instapaper.com/read/1934584443
politia rutiera
References:
https://v3.volshebnyj-uchastok-lorfilm.bio/user/maettewhbf
santa ana star casino
References:
https://ilovekino.online/user/vaginaostx
diamond joes casino
References:
https://www.fastbookmarks.win/top-choice-premier-online-casino-for-aussie-pokies-and-huge-jackpots
london casino
References:
http://mihrabqolbi.com/librari/share/index.php?url=https://www.bookmarkmaster.win/five-fresh-aussie-online-casino-picks-for-2025
casino vacances
References:
https://celebsbiz.site/user/vestersaot
craps system
References:
https://camtalking.com/@dwightgrinder8
gala casino gibraltar
References:
https://git.gostacks.org/stefanwilmer4
Viagra Newark: ViagraNewark – Viagra Newark
accutane mexican pharmacy https://edpillsafib.com/# Ed Pills Afib
blackjack strategies
References:
http://47.102.215.212:46846/shoshanatareno
https://edpillsafib.xyz/# online ed pills
Ed Pills Afib: online prescription for ed – online erectile dysfunction pills